合成碳奈米粒子應用於螢光快篩臨床用藥deferasirox之血中濃度
合成碳奈米粒子應用於螢光快篩臨床用藥defera
現行「快篩」已是所有檢測的發展重點,例如COVID-19的病毒檢測,就希望以快篩的方式快速了解病人是否染疫,因此建立快速、及時、準確的快篩技術於診斷科學上已是相當重要的發展項目,而本研究即是開發一種可以快速且準確分析血漿中的deferasirox之技術。“Deferasirox”俗稱排鐵劑,常用於一些須輸血治療之疾病,以排除因輸血所造成的體內鐵離子過高的問題;但是太多的deferasirox又會造成過量鐵離子排除,並會造成肝臟與腎臟的毒性,因此即時監測deferasirox之血中濃度即是臨床治療相當重要的步驟。本研究開發只要單存攜帶一簡單之螢光儀,即可對病人測定deferasirox之血中濃度,可以快速得到結果,對於病人提供更快速的診斷且即時做相關對應變化,對於目前強調的精準醫療,可提供一個診斷平台。
本研究設計使用螢光奈米粒子「碳奈米點」(carbon dots, CDs)來進行deferasirox之血中濃度快篩。「碳奈米點」為近幾年來一種新穎的材料,其製備過程相較於一般奈米粒子便利,僅需利用單純物質甚至咖啡渣,即可製造出具有螢光之碳奈米點。碳奈米點是一種微小的碳奈米粒子,其大小範圍為1-10奈米,主要由碳原子構成,因此具有良好的導電性、高化學穩定性、環境汙染程度低、相當寬的光吸收帶及高螢光量子產率等特點;且碳材取得容易、價格低廉,因此製作成本相對其它種類的奈米量材料更便宜;由於以上的特性,使得「碳奈米點」為近年來越來越受重視與應用。

本研究以簡單的化學原料(尿素和檸檬酸),利用水熱法合成出高螢光之碳奈米點,之後將碳奈米點表面衍生接上多巴胺(dopamine),而此合成材料在於有銅離子存在之環境時,其螢光會被大量的淬滅,但當有deferasirox存在時,其淬滅的螢光又可以恢復,且具有專一性,因此即可利用表面衍生化之碳奈米點的螢光恢復程度,應用於專一且快速的定量deferasirox;且該檢測皆使用血漿檢體進行,並不會因血漿中的雜質干擾而影響deferasirox之偵測。本法最後也應用到真實服用deferasirox之病人,其所偵測到之deferasirox血中濃度與一般臨床檢測結果相符,該結果證實此方法可快速且專一性得檢測deferasirox血中濃度,不僅使檢測變得更快速且方便,也可利用快速的檢測結果做後續的治療或用藥評估,對於現代強調的精準醫療,可提供一個強而有力的檢測平台。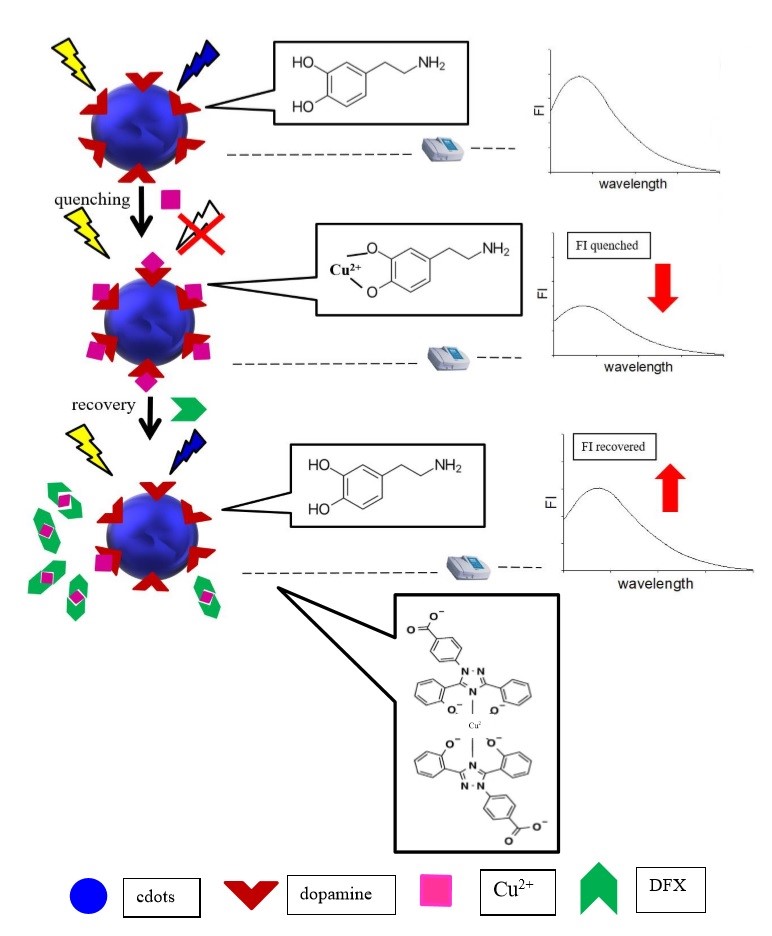
應用與亮點:
1.該表面衍生化之碳奈米點具有高螢光特性,可應用於多種領域。
2.此合成材料在於有銅離子存在之環境時,其螢光會被大量的淬滅,但當有deferasirox存在時,其淬滅的螢光又可以恢復,且具有專一性。
3.利用表面衍生化之碳奈米點的螢光恢復程度,可應用於專一且快速的定量deferasirox。
4.該法應用到真實服用deferasirox之病人,其所偵測到之deferasirox血中濃度與一般臨床檢測結果相符,該結果證實此方法可快速且專一性得檢測deferasirox血中濃度。
5.該法不僅使檢測變得更快速且方便,也可利用快速的檢測結果做後續的治療或用藥評估,對於現代強調的精準醫療,可提供一個強而有力的檢測平台。
【研究團隊】
團隊成員:王俊棋、黃柏蒼、柯黃盛、吳秀梅
代表單位:高雄醫學大學 藥學系
團隊簡介:該研究團隊長年來致力於毛細管電泳法、藥物分析、基因分析、特殊探針及引子設計、奈米粒子合成及應用等,已開發出多項藥物監測或基因檢測之技術,且獲得多項專利。
研究聯繫Email:chunchi0716@kmu.edu.tw
【論文資訊】
論文出處:Sensors & Actuators: B. Chemical, 2020, 311: 127916.
全文下載:https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0925400520302641
Synthesis of the carbon dots for fast fluorescently sensing deferasirox in plasma
Synthesis of the carbon dots for fast fluorescently sensing deferasirox in plasma
Currently, "quick screening" has been the focus of all testing development. For example, the virus detection of COVID-19, it is hoped to quickly understand whether a patient is infected with the disease in a quick screening method. Therefore, the rapid, timely and accurate quick screening technology has been fast developed in the diagnostic science. Therefore, this research is to develop a technology that can quickly and accurately analyze deferasirox in plasma. "Deferasirox" is commonly known as an iron excretion agent. It is often used in some diseases that require blood transfusion to eliminate the problem of excessive iron ions in the body. However, too much deferasirox will cause excessive iron ions to be eliminated and cause liver and renal toxicity. Thus, immediate monitoring of the blood concentration of deferasirox is a very important step in clinical treatment. In this research, the blood concentration of deferasirox can be easily measured on the patient just by a fluorescent spectrometer. The result can be obtained quickly, and the patient can be provided with more information. Rapid diagnosis and immediate corresponding changes can provide a diagnostic platform for the current emphasis on precision medicine.
This research is designed to use fluorescent nanoparticles, "carbon dots" (CDs) to quickly screen the blood concentration of deferasirox. CDs is a novel material in recent years, and its preparation process is more convenient than ordinary nanoparticle. Only simple substances or even coffee grounds can be used to produce fluorescent CDs. CDs are tiny carbon nanoparticles with a size range of 1-10 nanometers. They are mainly composed of carbon atoms. Therefore, they have good electrical conductivity, high chemical stability, low environmental pollution, and a wide range of light. CDs are easy to obtain and low in price, so the cost is cheaper than other kinds of nanometer materials. Due to the above characteristics, CDs have become more and more important and applicable in recent years.

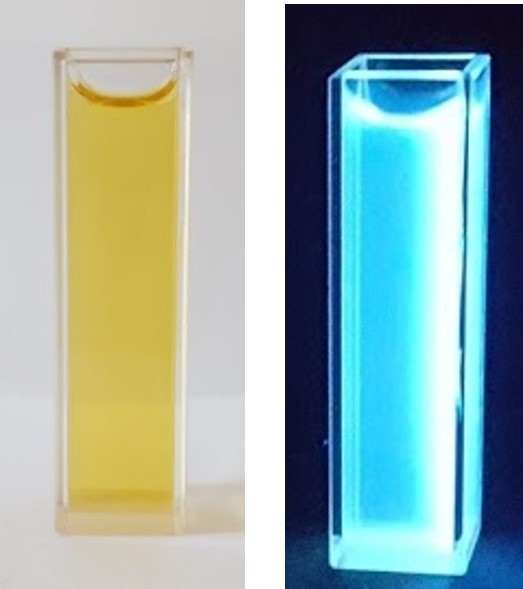
The color of the liquid after the synthesis of "carbon dots", and the strong fluorescence performance of the "carbon dots" under ultraviolet light.
This research uses simple chemical raw materials (urea and citric acid) to synthesize high-fluorescence CDs by hydrothermal method, and the CDs were then coated with dopamine. When the copper ions exist, fluorescence of CDs will be largely quenched. However, in the presence of deferasirox, the quenched fluorescence can be specifically restored. The degree of fluorescence recovery is used for specific and rapid quantification of deferasirox in plasma samples. Finally, this method was also applied to patients who actually took deferasirox. The detected blood concentration of deferasirox by this method was consistent with the clinical testing results. That confirmed that this method can quickly and specifically detect deferasirox in vivo, which not only makes the detection faster and more convenient, and the rapid test results can also be used for follow-up treatment or drug evaluation. For precision medicine, it can provide a powerful test platform.
Graphical Abstract

Application and Highlights:
1. The surface-derivative CDs have high fluorescent quantum yield and can be used in various fields.
2. When this CDs is in the presence of copper ions, its fluorescence will be largely quenched. However, when deferasirox is present, its quenched fluorescence can be specifically restored.
3. By using the fluorescence recovery degree of CDs, the deferasirox in plasma can be specifically and fast quantified.
4. This method was also applied to patients who actually took deferasirox. The detected blood concentration of deferasirox by this method was consistent with the clinical testing results.
5. This method not only makes the detection faster and more convenient, but can also use the rapid detection results for follow-up treatment or medication evaluation. It can provide a powerful detection platform for precision medicine.
Research Team Members:Chun-Chi Wang, Po-Tsang Huang, Hwang- Shang Kou, Shou-Mei Wu
Representative Department:School of Pharmacy, College of Pharmacy, Kaohsiung Medical University
Introduction of Research Team: The team has been committed to capillary electrophoresis, pharmaceutical analysis, genetic analysis, special probe and primer design, nanoparticle synthesis and application, etc. for many years. They have developed a number of technologies for drug monitoring or genetic testing, and obtained a number of patents.
Contact Email: chunchi0716@kmu.edu.tw
Publication:Sensors & Actuators: B. Chemical, 2020, 311: 127916.
Full-Text Article: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0925400520302641


