空氣污染因子透過芳香烴受體造成急性淋巴性白血病產生
空氣污染因子透過芳香烴受體造成急性淋巴性白血病產生
急性淋巴性白血病是兒童最常見的癌症,又以B 細胞前體急性淋巴細胞白血病 (BCP-ALL) 占大多數,這些細胞起源於骨髓中的淋巴前體細胞,屬於 B 細胞譜系。先前研究發現環境因素和遺傳異常會干擾這些前體細胞的正常成熟,促進前體細胞的癌化並抑制正常的造血功能,隨著人們現代化的生活,BCP-ALL 的發病率似乎也在增加,然而癌化進程的機制尚不清楚,研究假設空氣污染和霧霾是 BCP-ALL 進展的危險因子。由細胞實驗以及動物實驗發現,空氣汙染主要分子多環芳烴(PAHs)的主要成分Indeno[1,2,3-cd]pyrene(IP),能促進細胞致癌活性(增殖、轉型和疾病復發),是藉由活化芳香烴受體 (AHR)- 吲哚胺2,3-雙加氧酶 (IDO) 調控路徑,進而增強色氨酸代謝和犬尿氨酸 (KYN) 水平,促進 KYN-AHR 反饋迴路。原位異種移植小鼠模型研究也發現IP增加了BCP-ALL 細胞數並促進白血病復發。此外,臨床樣本也發現,AHR 和 IDO 的表現與疾病發展有相關性,且與無病存活期顯著相關。這些研究結果表明暴露空氣污染物質下,會促進急性淋巴性白血病產生。
圖形摘要
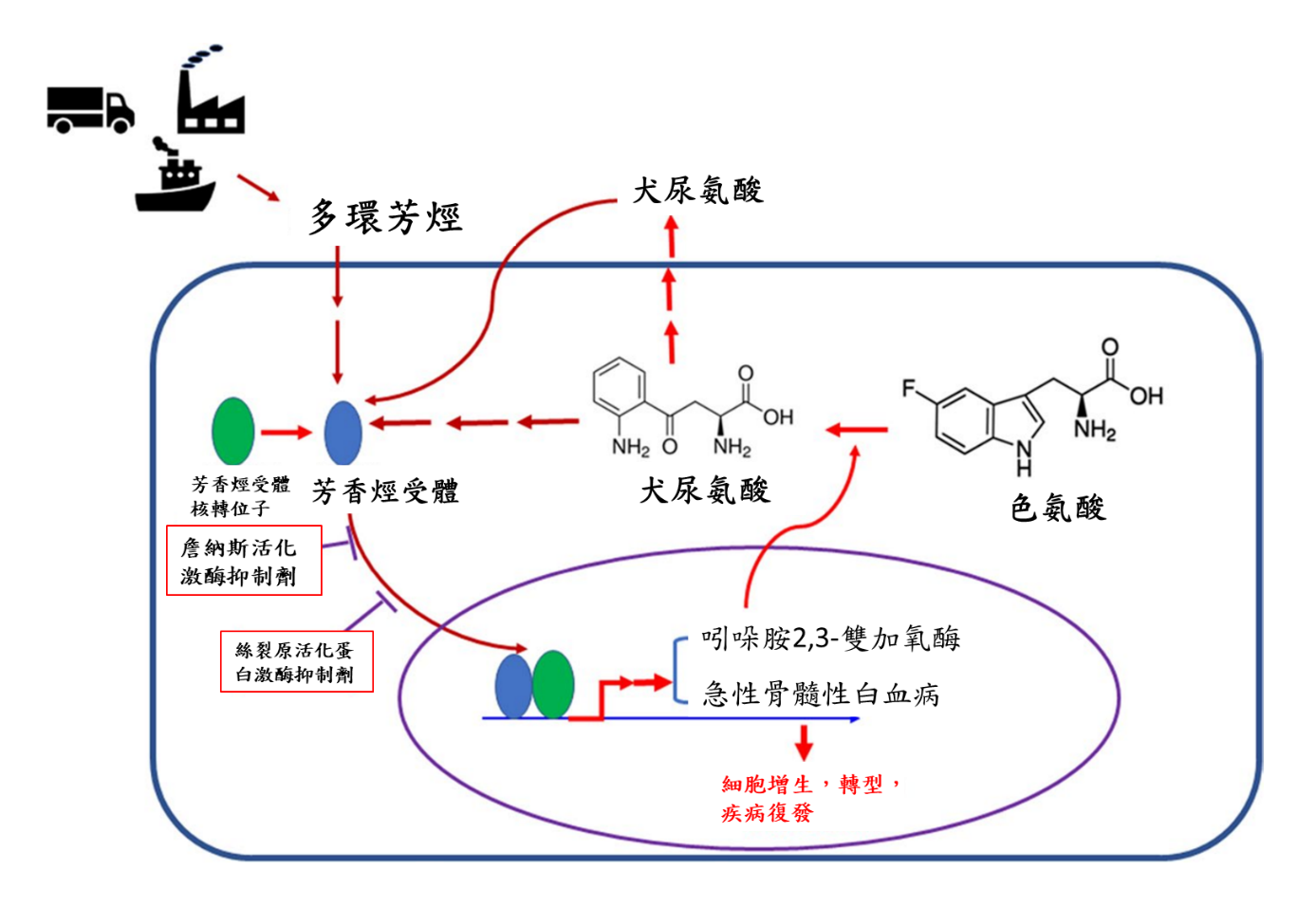
【應用與亮點】 本研究發現空氣污染造成急性淋巴性白血病產生的原因,對於後續研究相關基因調控路徑的抑制劑開發,提供明確的方向,對治療白血病開啟另一方針。
【團隊成員】本論文主要研究者邱世欣教授
【代表單位】高雄醫學大學應用基因體研究中心
研究聯繫Email:genomics@kmu.edu.tw
【論文資訊】
論文出處:Cell Biol Toxicol . 2022 Jun 10. doi: 10.1007/s10565-022-09734-0.
全文下載:https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s10565-022-09734-0
Air pollution factors cause acute lymphoblastic leukemia through aryl hydrocarbon receptor
Air pollution factors cause acute lymphoblastic leukemia through aryl hydrocarbon receptor
Acute lymphoblastic leukemia is the most common cancer in children and is dominated by B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia (BCP-ALL), which originate from lymphoid precursor cells in the bone marrow and belong to the B-cell lineage. Previous studies have found that environmental factors and genetic abnormalities interfere with the normal maturation of these precursor cells, promote their cancerization and inhibit normal hematopoiesis, and the incidence of BCP-ALL appears to be increasing as people modernize their lives, However, the mechanism of carcinogenesis remains unclear, and studies have hypothesized that air pollution and haze are risk factors for the progression of BCP-ALL. Cell experiments and animal experiments have found that Indeno[1,2,3-cd]pyrene (IP), the main component of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs), the main molecule of air pollution, can promote cell carcinogenic activity (proliferation, transformation and disease recurrence), By activating the aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AHR)-indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO) regulatory pathway, it enhances tryptophan metabolism and kynurenine (KYN) levels and promotes KYN-AHR feedback loop. Orthotopic xenograft mouse model studies also found that IP increased BCP-ALL cell numbers and promoted leukemia relapse. In addition, clinical samples also found that AHR and IDO manifestations were correlated with disease progression and significantly correlated with disease-free survival. These findings suggest that exposure to air pollutants can promote the development of acute lymphoblastic leukemia.
Graphical Abstract
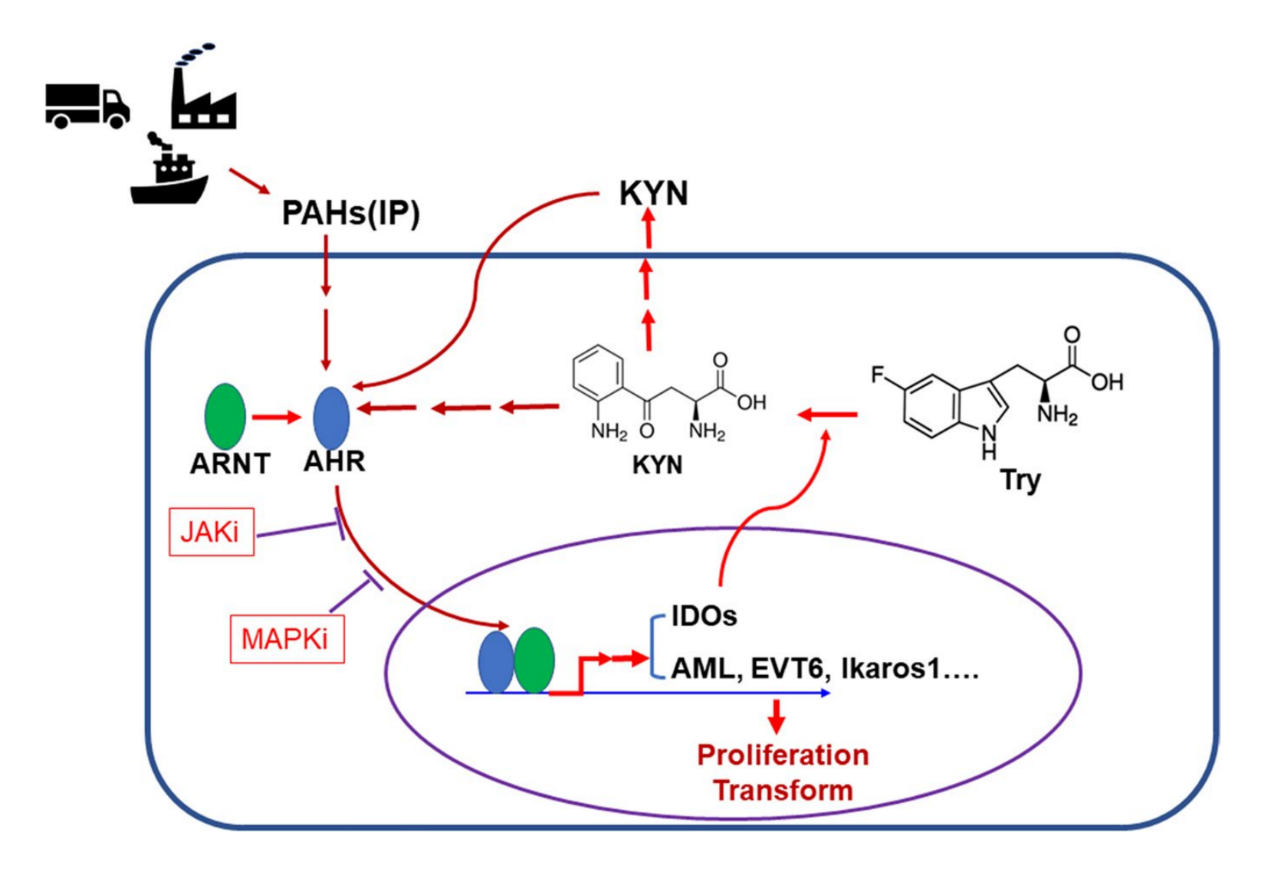
Main researcher :
Professor Shyh‑Shin Chiou, Center of Applied Genomics, Kaohsiung Medical University
Main authors’email :
genomics@kmu.edu.tw
Paper cited from :
Wang, L. T., Liu, K. Y., Wang, S. N., Lin, M. H., Liao, Y. M., Lin, P. C., Huang, S. K., Hsu, S. H., & Chiou, S. S. (2022). Aryl hydrocarbon receptor-kynurenine axis promotes oncogenic activity in BCP-ALL. Cell biology and toxicology, 10.1007/s10565-022-09734-0. Advance online publication. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10565-022-09734-0
Research Paper available online on website :
https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s10565-022-09734-0


