高血糖使HIF-1α過度表現導致接受術前同步放射線化學藥物治療的直腸癌抗性增加
高血糖使HIF-1α過度表現導致接受術前同步放射線化學藥物治療的直腸癌抗性增加
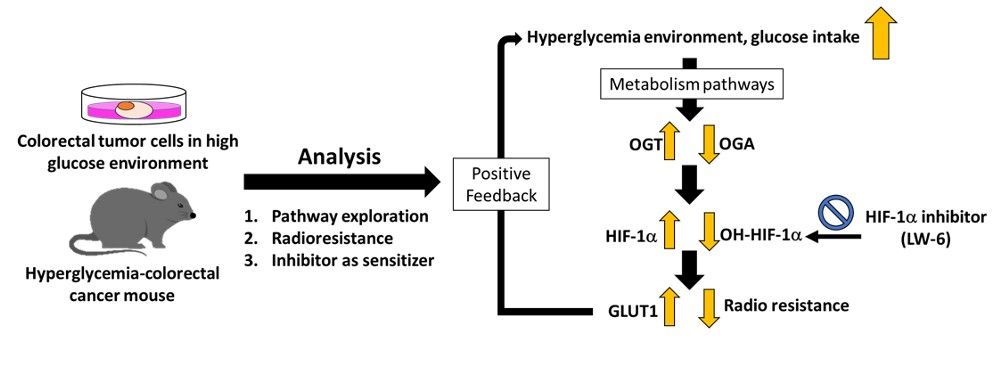
全球高血糖結直腸癌患者數量逐年增加。術前CCRT是局部晚期直腸癌患者的標準治療方法。然而,在高血糖結直腸癌患者中發現CCRT治療效果不佳。因此,我們調查了高血糖對結直腸癌CCRT抗性的影響。本研究調查了正常血糖及高血糖直腸癌患者接受CCRT治療後的預後指標。結果指出相較於正常血糖者(n = 41, HbA1c ≤6.4%)而言,高血糖直腸癌患者(n=13,糖化血紅蛋白,HbA1c>6.5%)預後指標較差,其中包含:腫瘤消退反應差(P=0.017),完全緩解率低(P=0.047),病理T分期較高(P=0.012)。此外,在高血糖結直腸癌患者中也有更高的HIF-1α表現(P=0.046)、並有更多的淋巴血管浸潤(P=0.009)、神經周圍浸潤(P=0.002)、腫瘤消退評分低(P=<0.001)及不完全緩解率(P=0.01)都有顯著相關性。因此,明確HIF-1α與接受術前CCRT的高血糖患者不良反應之間的關係非常重要。在高糖環境下,結直腸癌細胞會表達更高的葡萄糖轉運蛋白1(GLUT1)、O-GlcNAc轉移酶(OGA)和缺氧誘導因子-1α(HIF-1α)。相反,OGT 和 HIF-1α-OH 的表達下調,顯示高糖環境可能通過 GLUT1-OGA-HIF-1α 通路刺激 HIF-1α 表達,從而促進5-氟尿嘧啶 和放射線的耐受性(RT)。再者,在高血糖結直腸癌動物模型中,證實在高血糖的環境中會誘導結直腸癌細胞產生HIF-1α來減少細胞接受放射線所誘導的凋亡。進一步透過結合 HIF-1α 抑制劑可逆轉高葡萄糖環境中的放射抗性,因較低的 HIF-1α 水平增加了腫瘤中的 DNA 損傷導致細胞凋亡。以上的發現表明高血糖能誘導 OGT 和 HIF-1α 的表達提升結直腸癌中放射線的耐受,並表明聯合 HIF-1α 抑制劑可以逆轉高葡萄糖環境中的放射抗性。將來,也許 HIF-1α 抑制劑可用作高血糖結直腸癌患者的 CCRT增敏劑。
圖形摘要
應用與亮點:
1.確認高血糖環境能透過活化GLUT1-OGT-HIF-1a訊息傳導路徑導致放射線與化學治療藥物的抗性。
2. HIF-1a抑制劑的使用能降低其放化療之抗性。
【研究團隊】
團隊成員:莊智弘、黃旼儀
代表單位:高雄醫學大學醫學檢驗暨生物技術學系
團隊簡介:本團隊著重於代謝症候群與癌症療效相關性的研究
研究聯繫Email:a4132600@gmail.com
【論文資訊】
論文出處:Cancers (Basel). 2022 Aug 22; 14(16):4053.
全文下載:https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6694/14/16/4053
Hyperglycemia aggravates HIF-1α overexpression to promote preoperative concurrent chemoradiotherapy resistance in rectal cancer
Hyperglycemia aggravates HIF-1α overexpression to promote preoperative concurrent chemoradiotherapy resistance in rectal cancer
Purpose: Preoperative concurrent chemoradiotherapy (CCRT) is the standard treatment for patients with locally advanced rectal cancer. However, poor therapeutic efficacy of CCRT was found in rectal cancer patients with hyperglycemia.
Experimental Design: In this study, we investigated how hyperglycemia affects radiochemotherapy resistance in rectal cancer, including in clinical, in vitro, and in vivo.
Results: The prognosis indexes of euglycemic or hyperglycemic rectal cancer patients after receiving CCRT treatment were investigated. The hyperglycemic rectal cancer patients (n=13, glycosylated hemoglobin, HbA1c>6.5%) had poorer prognosis indexes. In addition, a positive correlation was observed between HIF-1α expression and HbA1c levels (P=0.046). Therefore, it is very important to clarify the relationship between HIF-1α and poor response in patients with hyperglycemia receiving pre-operative CCRT. Under a high glucose environment, rectal cancer cells express higher levels of glucose transport 1 (GLUT1), O-GlcNAc transferase (OGT), and hypoxia-inducible factor 1α (HIF-1α), suggesting the high glucose environment might stimulate HIF-1α expression through the GLUT1-OGT-HIF-1α pathway promoting tolerance to 5-FU and radiation. In the hyperglycemic rectal cancer animal model, rectal cancer cells confirmed that radiation exposure reduces apoptosis by overexpressing HIF-1α. Combining HIF-1α inhibitors was able to reverse radioresistance in a high glucose environment. Lower HIF-1α levels increased DNA damage in tumors leading to apoptosis.
Conclusions: The findings here show that hyperglycemia induces the expression of GLUT1, OGT and HIF-1α to cause CCRT tolerance in rectal cancer and suggest that combining HIF-1α inhibitors could reverse radioresistance in a high glucose environment. HIF-1α inhibitors may be useful for development as CCRT sensitizers in patients with hyperglycemic rectal cancer.
Graphical Abstract

Application and Highlights: (List)
1.Hyperglycemic environment causes to radioresistance in rectal cancer via activating the GLUT1-OGT-HIF-1a signal
pathway.
2.HIF-1a inhibitors reduce the radiotherapy resistance of rectal cancer caused by the hyperglycemic environment.
Research Team Members:
Chih-Hung Chuang,Ming-Yii Huang
Representative Department: Department of Medical Laboratory Science and Biotechnology, Kaohsiung Medical University, Kaohsiung 80708, Taiwan
Introduction of Research Team: Our team focuses on the correlation between metabolic syndrome and cancer response.
Contact Email: a4132600@gmail.com
Publication: Cancers (Basel). 2022 Aug 22; 14(16):4053.
Full-Text Article: https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6694/14/16/4053

