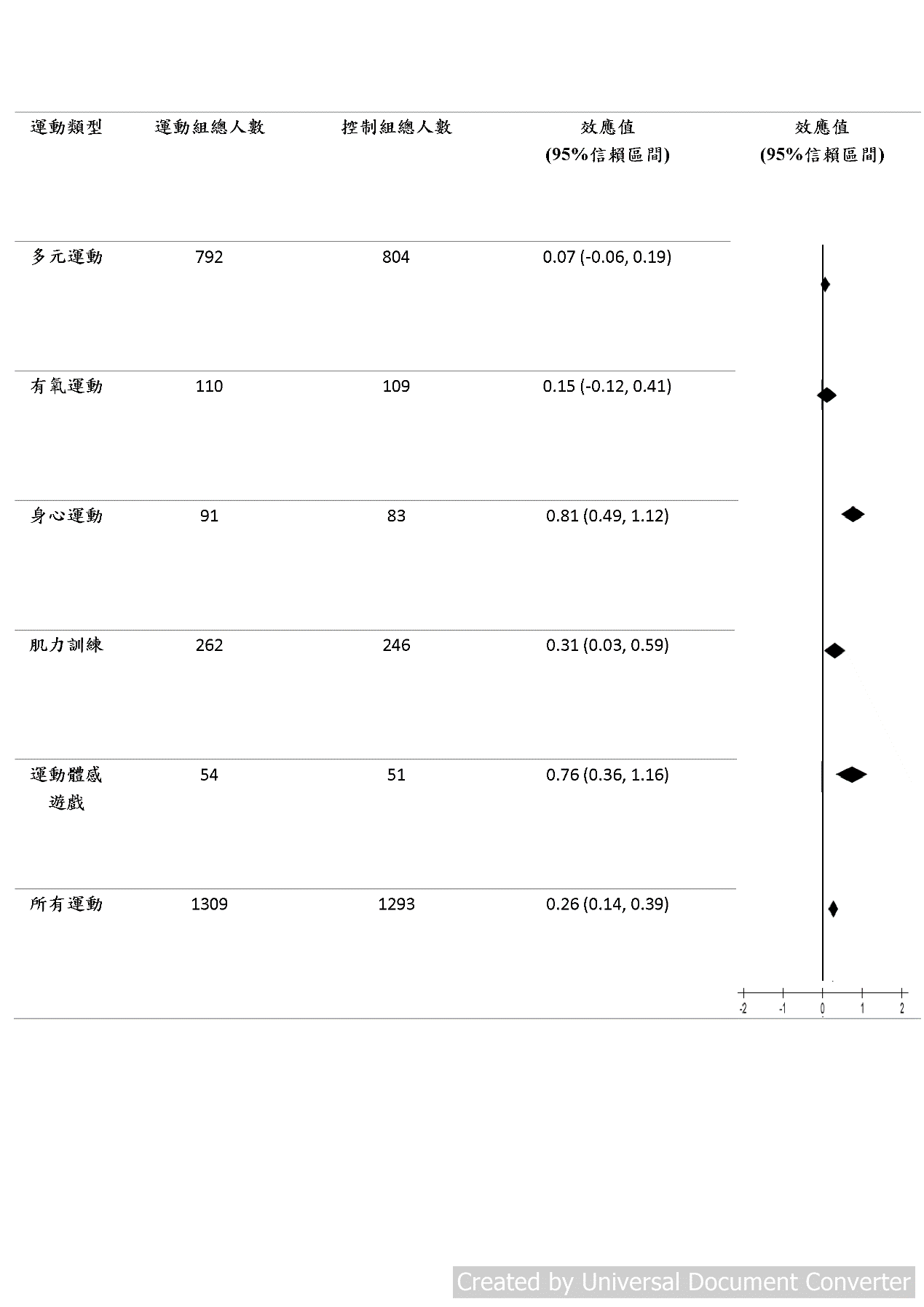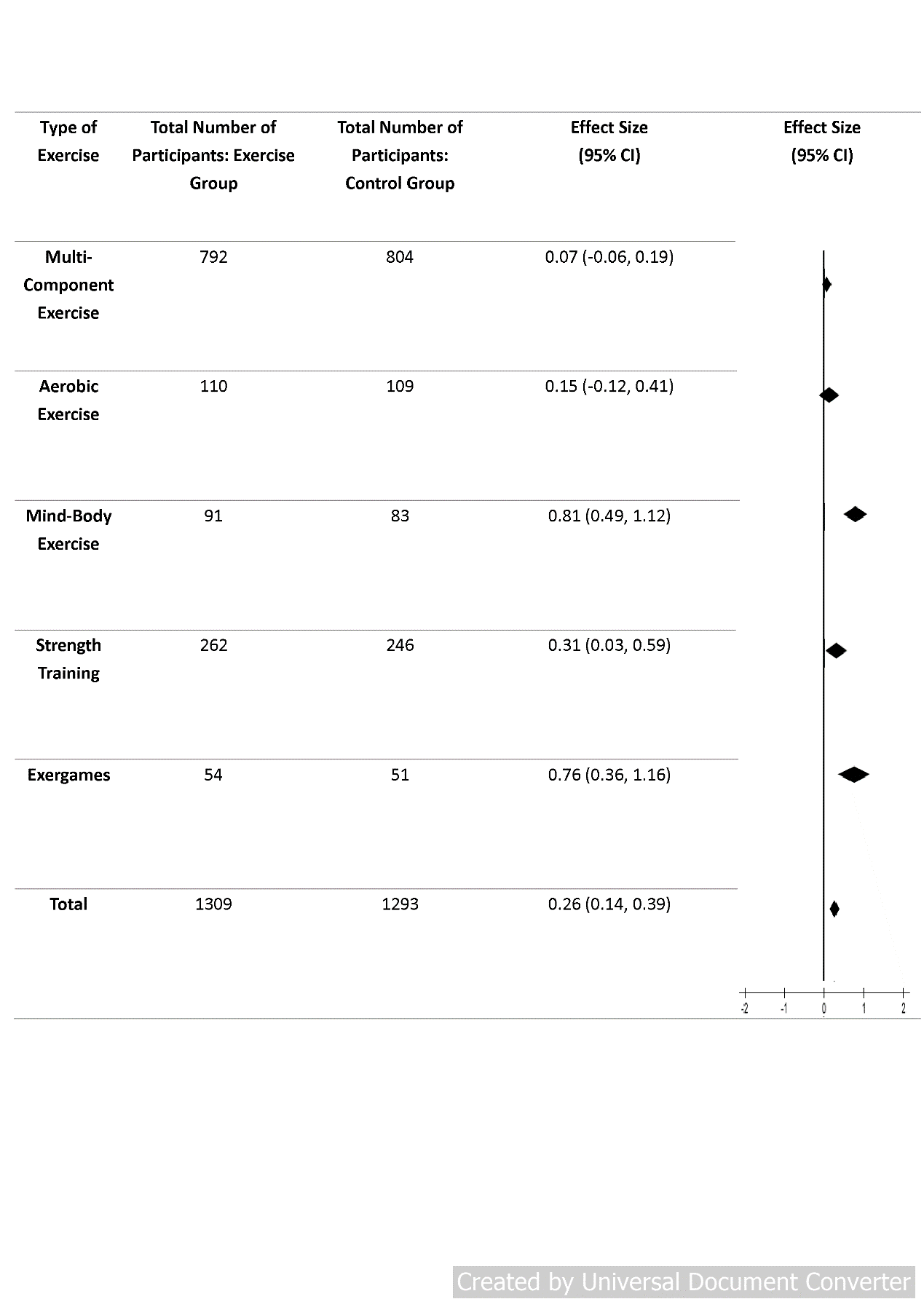以運動減緩長期照護機構住民的憂鬱症狀:不同種類及時間的運動效果
以運動減緩長期照護機構住民的憂鬱症狀:不同種類及時間的運動效果
根據世界衛生組織2017年的報告,全世界有高達2.64億人正受憂鬱所困,而其中7%的患者為65歲以上的老年人。其中,居住於長期照護機構的老年人更加容易因為與家人分離以及家庭角色的變化產生憂鬱的症狀。研究指出,運動能有效緩解憂鬱對老年人所產生的不良影響;然而,相較於健康的老年人,居住於長期照護機構的老年人容易因為營養不良或是認知、肢體功能的退化而無法負荷傳統的運動介入。因此,運動介入是否可以改善居住於長期照護機構老年人的憂鬱症狀仍未有定論。
本研究以系統性回顧配合統合分析方式,檢視了7,569篇有關的文獻。在經過題目、研究內容與研究品質的仔細篩選後,選取了25篇內容為分析不同運動介入在長期照護機構老年住民之憂鬱症狀影響的文獻納入系統性回顧,並取其中的22篇進一步進行統合分析。這些文獻中所納入的研究對象包括了居住於長期照護機構認知功能完好以及認知功能受限的老年人。而研究中所使用的運動種類包括多元運動、有氧運動、肌力訓練、身心運動(例如瑜珈、皮拉提斯)以及體感運動遊戲。統合分析的結果顯示,不管認知功能是否完好,運動介入皆能改善長期照護機構住民的憂鬱症狀。進一步針對不同運動種類的分析則顯示,身心運動、體感運動遊戲以及肌力訓練改善憂鬱症狀的效果最佳。
這份系統性回顧及統合分析的研究指出,居住於長期照護機構的老年人,不管是否有認知功能上的減損,規律的運動皆能有效的緩解憂鬱症狀並降低憂鬱症狀所產生的影響。而其中身心運動、體感運動遊戲以及肌力訓練較為適合居住於長期照護機構的老年人。未來可根據這些方向設計適合長期照護機構住民的運動介入活動。
圖形摘要
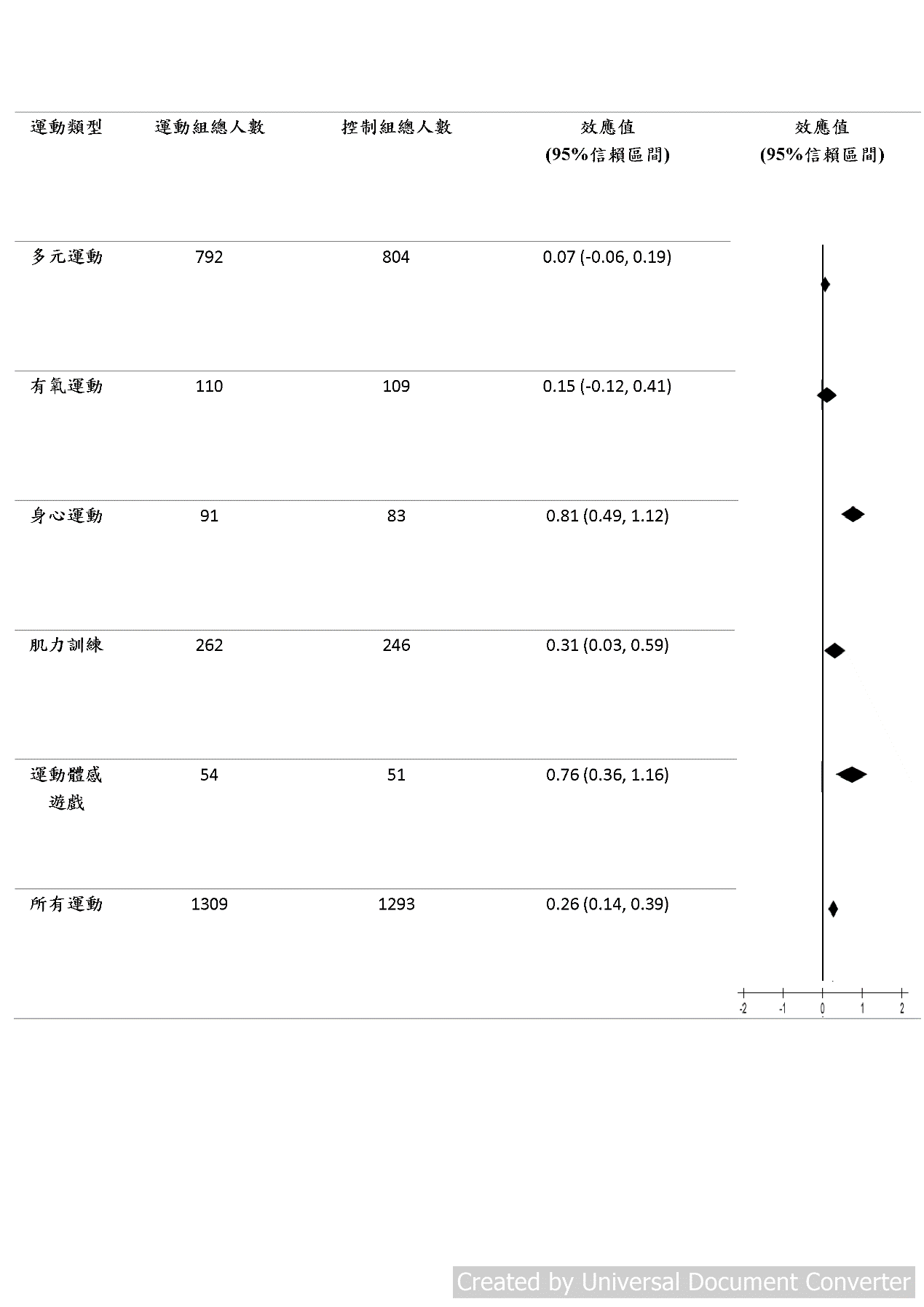
應用與亮點:
1.運動介入可以緩解居住在長期照護機構的老年人可能患有的憂鬱症狀。
2. 在不同種類的運動介入中,身心運動、肌力訓練以及體感運動遊戲在緩解居住於長期照護機構之老年人憂鬱症狀效果最佳。
【研究團隊】
團隊成員:陳桂敏教授、陳柏榕博士、許慧芬博士、Frank Belcastro教授
代表單位:長期照顧研究中心
團隊簡介:陳桂敏教授帶領的研究團隊長期致力於老年人之長期照護研究與服務,研究方向包括應用於老年人之健康促進策略、老年人適用之運動方式與活動設計、輔助/另類療法開發、老人護理與長期照護之相關研究。
研究聯繫Email:kmc@kmu.edu.tw
【論文資訊】
論文出處:Chen, P. J., Chen, K. M., Hsu, H. F., & Belcastro, F. (2022). Types of exercise and training duration on depressive symptoms among older adults in long-term care facilities. Ageing Research Reviews, 101613. (SCI; Impact factor: 11.788)
全文下載:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arr.2022.101613
The effects of different physical exercise programs and training durations in managing depression of older adults living in long-term care facilities
The effects of different physical exercise programs and training durations in managing depression of older adults living in long-term care facilities
According to the World Health Organization (WHO, 2017), more than 264 million people are affected by depression worldwide, and 7% of them are older adults over 65 years old. In particular, older adults living in long-term care facilities (LTCFs) are more susceptible to depression due to their separation from family members and changes in family role. Current evidence suggests that physical exercise intervention can effectively counter the negative influence of depression in older adults. However, older adults living in LTCFs may not tolerate regular exercise programs that are designed for healthy older adults, as they are more susceptible to malnutrition and the decline of cognitive and physical function. Thus, it remains unclear whether physical exercise can alleviate depression for older adults living in LTCFs.
Our systematic review and meta-analysis identified 7,569 relevant publications, and after careful evaluation, 25 articles were selected for our systematic review and 22 articles for the meta-analysis. The included studies investigated the effects of different physical exercise in older adults living in LTCFs, including those with cognitive impairments. The types of physical exercise carried out in these studies included multi-component exercise, aerobic exercise, strength training, mind-body exercises (e.g. yoga or Pilates) and exergames. The results of our meta-analysis indicated that regardless of cognitive impairment, physical exercise was effective in mitigating depressive symptoms in older adults living in LTCFs. Further analysis revealed that mind-body exercise, exergames, and muscle strengthening exercise were the most effective types of exercise in mitigating depressive symptoms.
Our findings suggest that older adults living in LTCFs, regardless of cognitive impairments, should perform physical exercise regularly to mitigate the symptoms of depression. In regards to the type of physical exercise, mind-body exercise, exergames, and muscle strengthening exercise are more appropriate for older adults living in LTCFs. These findings can provide direction for future developments of physical exercise programs for older adults living in LTCFs.
Graphical Abstract
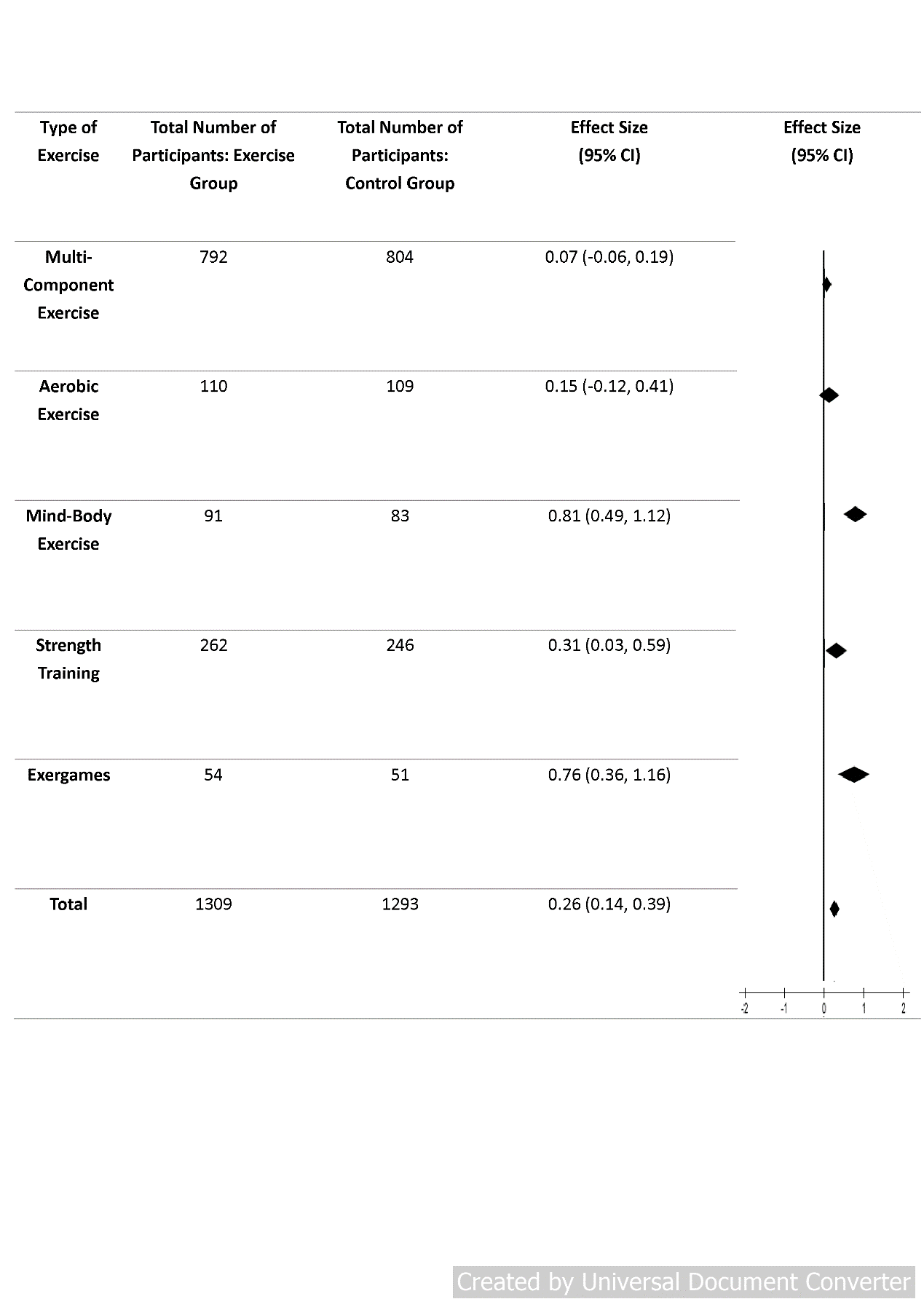
Applications and Highlights:
1.Physical exercise is effective in mitigating depression of older adults living in long-term care facilities.
2.Among different types of physical exercise, mind-body exercise, exergames, and muscle strengthening exercise are most effective in
mitigating depression of older adults living in long-term care facilities.
【Research Team】
Members: Professor Kuei-Min Chen, Dr. Po-Jung Chen, Dr. Hui-Fen Hsu, Professor Frank Belcastro
Representative Department: Center for Long-term Care Research
Introduction of Research Team: The research team lead by Professor Kuei-Min Chen has long been focusing on research and clinical services for older adults and long-term care sector. The research topics emphasize on health promotion programs for older adults, designing physical exercise programs for older adults, complementary and alternative therapies applications, and a wide array of topics associated with long-term care in aging.
Contact Email: kmc@kmu.edu.tw
【Article Information】
Chen, P. J., Chen, K. M., Hsu, H. F., & Belcastro, F. (2022). Types of exercise and training duration on depressive symptoms among older adults in long-term care facilities. Ageing Research Reviews, 101613. (SCI; Impact factor: 11.788)
Link for full-text: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arr.2022.101613