建立單鹼基對錯配 PCR技術搭配磁珠基因捕捉平台應用於快速檢測K-RAS 基因上之密碼子 12 和 13遺傳變異
建立單鹼基對錯配 PCR技術搭配磁珠基因捕捉平台應用於快速檢測K-RAS 基因上之密碼子 12 和 13遺傳變異
近幾年來,由於大眾開始對健康與預防醫學的重視,使得【基因檢測】成為相當被重視的國家發展主題與學術研究項目。基因檢測(Genetic Test)是偵測染色體結構中之DNA序列是否存在變異位點或探討基因的表現程度,提供受檢者與醫療研究人員評估一些基因遺傳相關疾病、體質或個人特質的依據,也是精準醫學檢測的一種方法。目前國內也積極發展”精準醫療”,其中一項即是應用基因檢測進行序列比對,呈現基因的變異狀態,希望能夠幫助預測罹患疾病的風險、診斷疾病進程、分析預後及精準的治療等等,且能進一步結合流行病學、分子醫學等研究綜合評估罹患疾病及健康問題等風險,進而選擇最適當預防策略或治療規劃。近幾年來,臺灣積極發展精準醫療,亦稱個人化醫療,為考量個體或特定族群之基因組成、背景環境及生活型態等因素,訂出合適精確的疾病預防、診斷與治療計畫。
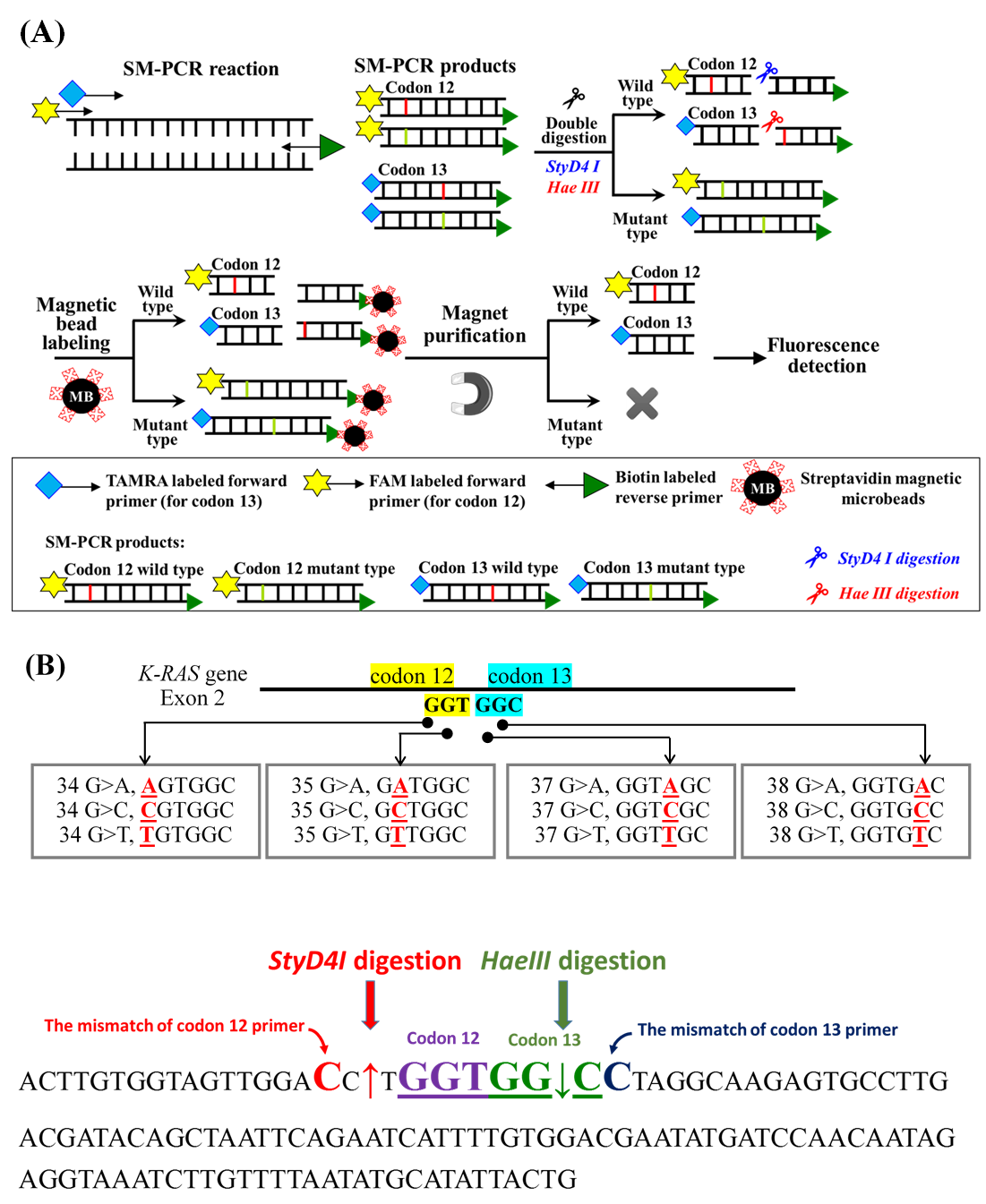
然而,現行基因檢測技術經常需要使用到一些昂貴耗材或大型儀器等,因此並非所有實驗室可執行相關之基因檢驗技術,而為了使得基因檢測技術更簡單、方便、準確且快速,本研究開發一『單鹼基對錯配 PCR技術搭配磁珠基因捕捉平台』,並應用於快速檢測K-RAS 基因上之密碼子 12 和 13遺傳變異,其檢測原理如圖形摘要所示。本方法於PCR之引子設計時,會於靠近基因變異處刻意設計1鹼基對與真實基因錯配,此錯配之引子將基因放大後,其基因序列即會含有錯配之鹼基對,之後應用streptavidin修飾之磁珠將此錯配鹼基對之放大基因片段捕捉與純化,最後即可利用錯配之鹼基對搭配所含之基因變異,設計限制酶酵素只將要分析的基因型放大片段分解。此時,含有FAM或TAMRA螢光基團的另一端即會釋放到液體當中,因此只要分析液體的螢光強度,即可了解K-RAS 基因上之密碼子 12 和 13為何種基因型,且本研究成功得以單一技術同時分析K-RAS 基因上之密碼子 12 和 13上之2個基因變異點位。
此方法方便、簡單且快速,且該方法具有通用性,只要設計適當的錯配引子及適合的限制酶酵素即可應用於不同基因之檢測,相當地適合應用於分析各種不同類型的基因變異。
圖形摘要
應用與亮點:
1.本研究以單一鹼基對錯配引子搭配 PCR技術創造出可以限制酶酵素辨識之基因點位,增加基因辨識之方便性。
2.本研究成功得以單一技術並應用FAM及TAMRA之2種不同螢光基團,同時分析K-RAS 基因上之密碼子 12 和 13上之2個基因變異點
位。
3.此方法方便、簡單且快速,且該方法具有通用性,只要選擇適當的限制酶酵素即可應用於不同基因之檢測,相當地適合應用於分析
各種不同類型的基因變異。
【研究團隊】
團隊成員:潘姿羽、柯黃盛、吳秀梅、王俊棋
代表單位:高雄醫學大學 藥學系
團隊簡介:該研究團隊長年來致力於毛細管電泳法、藥物分析、基因分析、特殊探針及引子設計、奈米粒子合成及應用等,已開發出多項藥物監測或基因檢測之技術,且獲得多項專利。
研究聯繫Email:chunchi0716@kmu.edu.tw
【論文資訊】
論文出處:Sensors & Actuators: B. Chemical, 2023, 382: 13517.
全文下載:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2023.133517
Fast genotyping of K-RAS codons 12 and 13 based on streptavidin magnetic microbeads equipped with biotin-coupled single base-pair mismatch PCR (SM-PCR)
Fast genotyping of K-RAS codons 12 and 13 based on streptavidin magnetic microbeads equipped with biotin-coupled single base-pair mismatch PCR (SM-PCR)
In recent years, as the public has begun to pay attention to health and preventive medicine, genetic testing has become a national development theme and academic research project that has received considerable attention. Genetic testing is to detect whether there are mutation sites in the DNA sequence in the chromosomal structure or to explore the expression level of genes. It provides the basis for the subjects and medical researchers to evaluate some genetically related diseases, physical fitness or personal characteristics. A method for precision medicine testing. At present, "precision medicine" is also actively developed, and one of which is the application of genetic testing for sequence comparison, showing the mutation status of genes, hoping to help predict the risk of disease, diagnose the disease process, analyze the prognosis and provide precise treatment, etc., and can further combine epidemiology, molecular medicine and other research to comprehensively assess the risk of suffering from diseases and health problems, and then choose the most appropriate prevention strategy or treatment plan. In recent years, Taiwan has actively developed precision medicine, also known as personalized medicine, to formulate appropriate and accurate disease prevention, diagnosis and treatment plans for individuals or specific ethnic groups based on factors such as their genetic makeup, background environment, and lifestyle.
However, the current genetic testing technology often requires the use of some expensive consumables or large-scale instruments, so not all laboratories can perform related genetic testing technology. In order to make the genetic testing technology simpler, more convenient, more accurate and faster, this research develops a "Single base pair mismatch PCR technology combined with magnetic bead gene capture platform", and applied to the rapid detection of genetic variation of codons 12 and 13 on the K-RAS gene, the detection principle is as shown in the graphic abstract. In this method, when designing primers for PCR, one base pair is deliberately designed to be mismatched with the real gene near the genetic variation. After the mismatched primer amplifies the gene, the gene sequence will contain the mismatched base pair. Then use streptavidin-modified magnetic beads to capture and purify the amplified gene fragments of the mismatched base pairs, and finally use the mismatched base pairs to match the gene variation contained in it, and design restriction enzymes to amplify only the genotype to be analyzed Fragmentation breaks down. At this time, the other end containing the FAM or TAMRA fluorescent group will be released into the liquid, so as long as the fluorescence intensity of the liquid is analyzed, the genotypes of codons 12 and 13 on the K-RAS gene can be known, and In this study, a single technique was successfully used to simultaneously analyze two genetic mutation points on codons 12 and 13 of the K-RAS gene.
This method is convenient, simple and fast, and the method is versatile, as long as proper mismatch primers and suitable restriction enzymes are designed. It can be applied to the detection of different genes, and is quite suitable for the analysis of various types of gene variation.
Graphical Abstract

Application and Highlights:
1. In this study, single base pair mismatch primers combined with PCR technology were used to create gene loci that can be identified by restriction enzymes, increasing the convenience of gene identification.
2. In this study, a single technique was successfully applied and two different fluorescent groups of FAM and TAMRA were used to simultaneously analyze two gene mutation points on codons 12 and 13 of the K-RAS gene.
3. This method is convenient, simple and fast, and this method is versatile. It can be applied to the detection of different genes as long as an appropriate restriction enzyme is selected, and it is quite suitable for the analysis of various types of gene variation.
Research Team Members: Tzu-Yu Pan, Hwang-Shang Kou, Shou-Mei Wu, Chun-Chi Wang
Representative Department: School of Pharmacy, College of Pharmacy, Kaohsiung Medical University
Introduction of Research Team: The team has been committed to capillary electrophoresis, pharmaceutical analysis, genetic analysis, special probe and primer design, nanoparticle synthesis and application, etc. for many years. They have developed a number of technologies for drug monitoring or genetic testing, and obtained a number of patents.
Contact Email: chunchi0716@kmu.edu.tw
Publication: Sensors & Actuators: B. Chemical, 2023, 382: 13517.
Full-Text Article: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2023.133517

