以愛玉枝葉萃取物進行緩解 COVID-19 併發症前驅藥物之研發
以愛玉枝葉萃取物進行緩解 COVID-19 併發症前驅藥物之研發
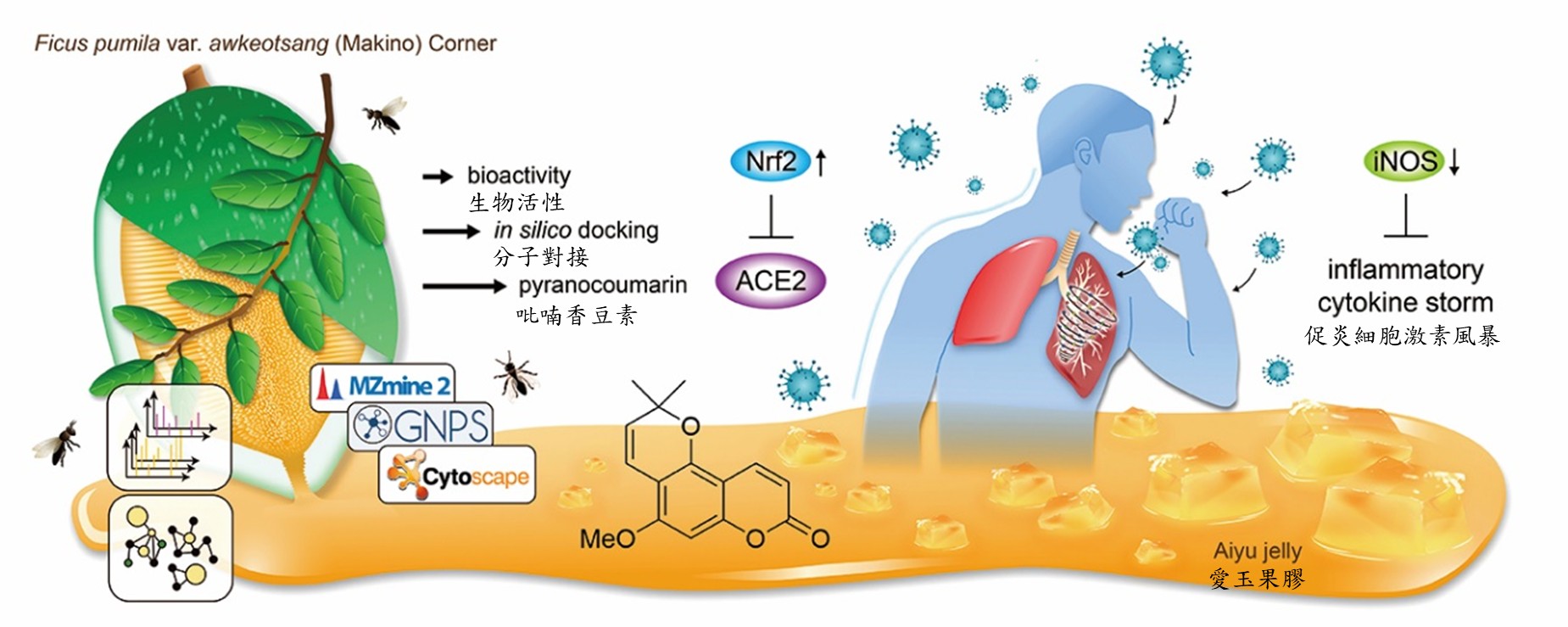
愛玉 (Ficus pumila var. awkeotsang) 為台灣特有亞種植物,是相當受到歡迎的飲品「愛玉」之原植物。由於愛玉種植時需去除多餘之枝葉,也是農民很大之工作負擔,基於循環經濟的概念,本團隊以愛玉之農業副產物-廢棄之枝葉進行研究。
從愛玉枝葉萃取物 (FPAT)中分離純化新的化學成分-ficumarin,以及其他主要抑制嗜中性白血球發炎之功效成分 alloxanthoxyletin、betulinic acid 和catechin 等。其中,發現功效最好的成分為 alloxanthoxyletin ,會與人類發炎有關的蛋白質 INOSOX 結構上的 PRO350 和 GLU377 胺基酸位點發生交互作用,結合後即會產生抑制發炎之作用。此外也證實 FPAT 和其香豆素類成分 (不是會致癌的香豆素喔! 是一類具有特殊骨架的化學成分) 具有活化生物自體抗氧化系統 Nrf2 的能力。Nrf2是調控細胞氧化應激反應的重要轉錄因子,同時也是維持細胞內氧化還原穩態的中樞調節者。另Nrf2是多種慢性發炎疾病的治療靶標,也參與細胞免疫、凋亡及腫瘤發生等多種進程,是最近幾年科學家一直在探討的熱門研究標的。我們很特別的發現愛玉枝葉萃取物,具有調控 Nrf2 之功效。
透過高解析度液相層析串聯質譜儀 LC-MS / MS和特徵分子網絡 GNPS 分析,發現香豆素類化合物為主要功效之成分。最新的研究發現 Nrf2 也與 COVID-19 有關,因此我們進一步發現 Alloxanthoxyletin可刺激 Nrf2 表達增加近八倍 (816.8±5%)。進一步利用 COVID-19 Docking Server 進行分子模擬的結果顯示,香豆素類化合物有望干擾SARS-CoV-2的生命週期。舉凡 GNPS 與 COVID-19 Docking Server 等資料庫,都是目前最流行的 AI 話題。這些大資料庫,使得世界無國界,科學家可以在實驗室上傳自己的數據,利用超級電腦等設備進行研究,這些系統也因為收集到全世界研究者的數據,而變得更加強大。例如,GNPS 系統,科學家可能只需要 1 毫克以下的樣品,即可推測一種萃取物中含有之化學成分, AI 之未來潛力無法計量 !
研究結果證明了FPAT對嗜中性白血球細胞具有抗炎作用並能活化Nrf2,因此有機會發展為 COVID-19 治療的補充輔助劑。然而,在使用之安全性與劑量方面需要進一步驗證與研究。
應用亮點:
1.愛玉枝葉農業副產物再生加值。
2.香豆素類化合物具抑制SARS-CoV-2生命週期之潛能。
3.利用愛玉研發 COVID-19 治療的補充劑。
【研究團隊】
團隊成員:
張芳榮教授、顏嘉宏教授、胡皓竣博士、余思穎博士、蔡逸宏助理教授
代表單位:高雄醫學大學新藥開發暨價創研究中心
團隊介紹:張芳榮教授團隊主要研究方向是小分子新藥開發、化粧品有效原料開發、中草藥活性與成分研究、機能性食品開發、表觀基因調控技術研發真菌功能性二次代謝物。
研究聯繫Email:aaronfrc@kmu.edu.tw
【論文資訊】
論文出處:JOURNAL OF FOOD AND DRUG ANALYSIS, 2022; 30:440–453
全文下載:https://doi.org/10.38212/2224-6614.3419
Developing Extracts of Branches and Leaves from Ficus pumila var. awkeotsang as a Mitigating Prophylactic Agent for COVID-19 Complications.
Developing Extracts of Branches and Leaves from Ficus pumila var. awkeotsang as a Mitigating Prophylactic Agent for COVID-19 Complications.
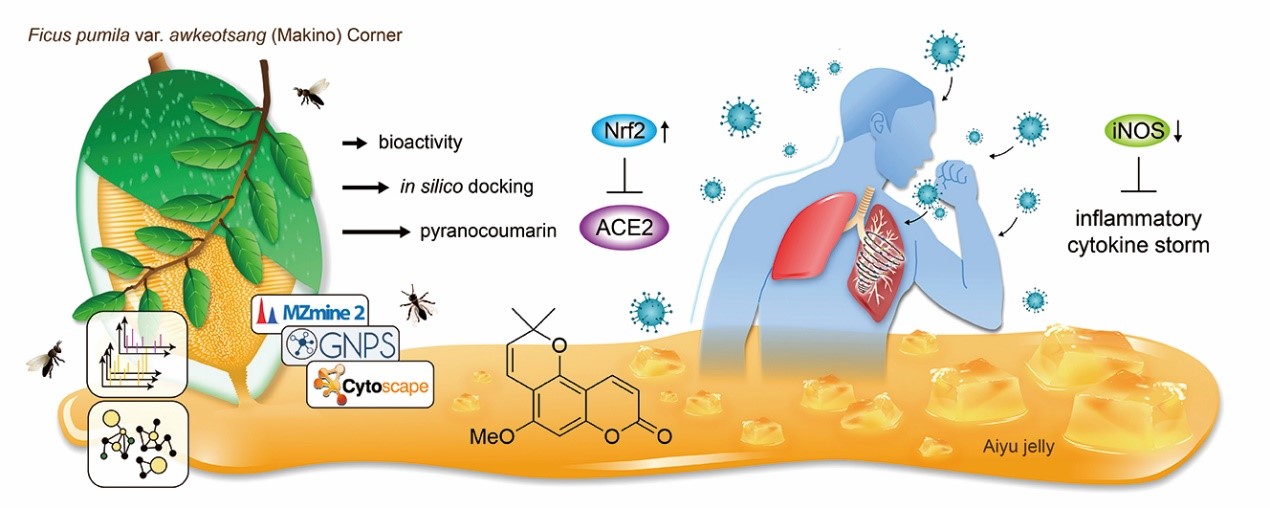
Aiyu (Ficus pumila var. awkeotsang) is a unique plant subspecies native in Taiwan, and serves as the original source for a popular food known as 'Aiyu Gelly'. During the cultivation of Aiyu, it involves in the removal of excess branches and leaves, which can be a huge work-loadings for farmers. Our research team, guided by the concepts of circular economy, undertook a study focusing on Aiyu's agricultural byproduct - discarded branches and leaves- as the target materials for further development.
From the extract of Aiyu branches and leaves (FPAT), we isolated and purified a novel chemical compound 'ficumarin', as well as anti-inflammatory bioactive components such as alloxanthoxyletin, betulinic acid, and catechin. Among these components, alloxanthoxyletin exhibited the most significant efficacy by interacting with specific amino acid residues, PRO350 and GLU377, within the INOSOX protein associated with human inflammation. This interaction leads to the inhibition of the inflammatory response.
Furthermore, our study confirmed that FPAT and its coumarin-type constituents (not the carcinogenic compound, coumarin. It is a series of compounds with a coumarin chemical skeleton.) possess the ability to activate Nrf2 in the antioxidant system. Nrf2 is a crucial transcription factor regulating cellular responses to oxidative stress and is a central regulator in maintaining cellular redox homeostasis. Nrf2 is also a therapeutic target for various chronic inflammatory diseases and plays a role in processes such as cellular immunity, apoptosis, and tumorigenesis. Interestingly, it is special that FPAT has the capacity to modulate Nrf2.
Through high-resolution liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) and feature-based molecular networking analysis in the Global Natural Products Social Molecular Networking (GNPS) platform, we identified coumarin-type compounds as the primary bioactive constituents. Recent research has indicated a link between Nrf2 and COVID-19. Consequently, we found that alloxanthoxyletin can stimulate an approximately eightfold increase (816.8±5%) in Nrf2 expression. Molecular simulations conducted using the COVID-19 Docking Server suggest that coumarin-type compounds hold promise in interfering with the life cycle of SARS-CoV-2. Databases like GNPS and COVID-19 Docking Server are currently at the forefront of AI-driven research. These extensive databases have made scientific collaboration borderless, allowing researchers to upload their data, harness the power of supercomputers, and conduct studies that were previously unimaginable. For instance, the GNPS system enables scientists to deduce the chemical composition of a sample less than 1 milligram, showcasing the limitless potential of AI.
Our research results demonstrate that FPAT exhibits anti-inflammatory effects on neutrophils, and has the capability to activate Nrf2. Therefore, there is potential for its development as a supplementary adjuvant for COVID-19 treatment. However, further research and verification are needed for its safety and toxicity in practical applications.
Application and Highlights:
1.Value-adding for Agricultural Byproducts of Aiyu Branch and Leaves.
2.Coumarin-Type Compounds Exhibit the Potential to Inhibit the Life Cycle of SARS-CoV-2.
3.Harnessing Aiyu as Supplementary or Therapeutic Agents for COVID-19.
Research Team Members:
Prof. Fang-Rong Chang, Prof. Chia-Hung Yen, Dr. Hao-Chun Hu, Dr. Szu-Yin Yu, Asst. Prof. Yi-Hong Tsai
Representative Department:
Drug Development and Value Creation Research Center, Kaohsiung Medical University
Introduction of Research Team:
The research team of Professor Fang-Rong Chang primarily focuses on the following research directions: Development of Novel Small-Molecule Pharmaceuticals, Effective Ingredients for Cosmetics, Research on the Activities and Constituents of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Development of Functional Foods, Research and Development of Epigenetic and Genetic Regulation Techniques on Functional Secondary Metabolites of Fungi.
Contact Email: aaronfrc@kmu.edu.tw
Publication: JOURNAL OF FOOD AND DRUG ANALYSIS, 2022; 30:440–453.
Full-Text Article: https://doi.org/10.38212/2224-6614.3419


