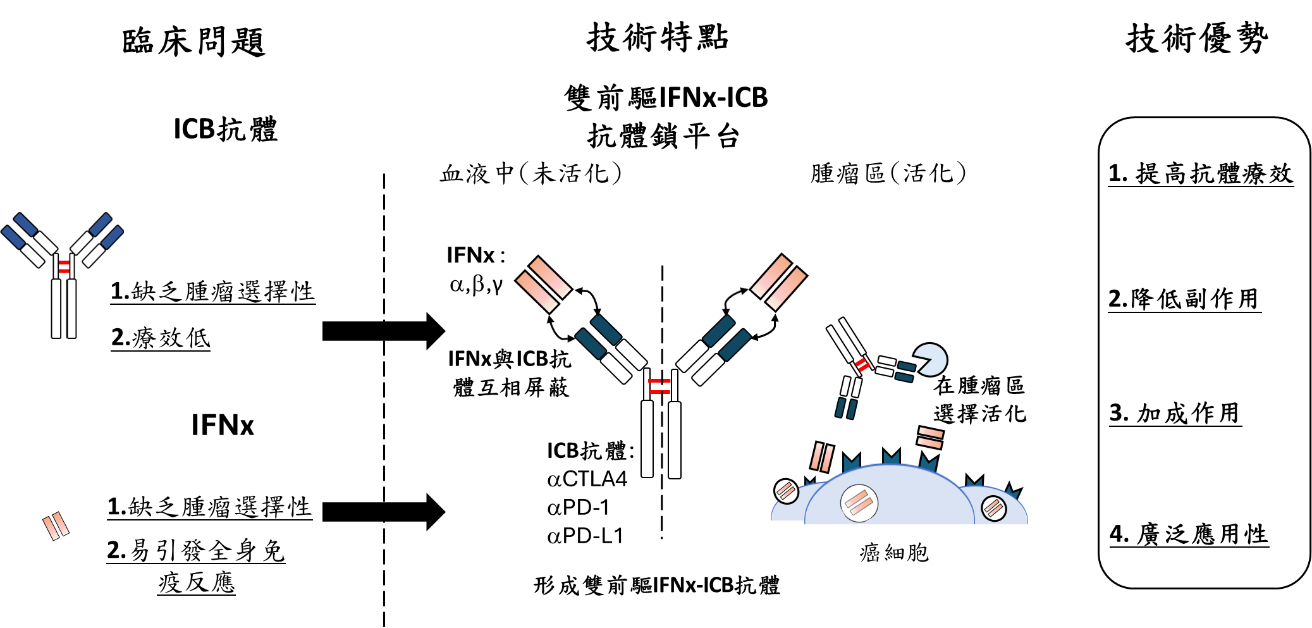
開發雙前驅IFNr- Ipilimumab抗體以提升臨床癌症治療效果和安全性
開發雙前驅IFNr- Ipilimumab抗體以提升臨床癌症治療效果和安全性
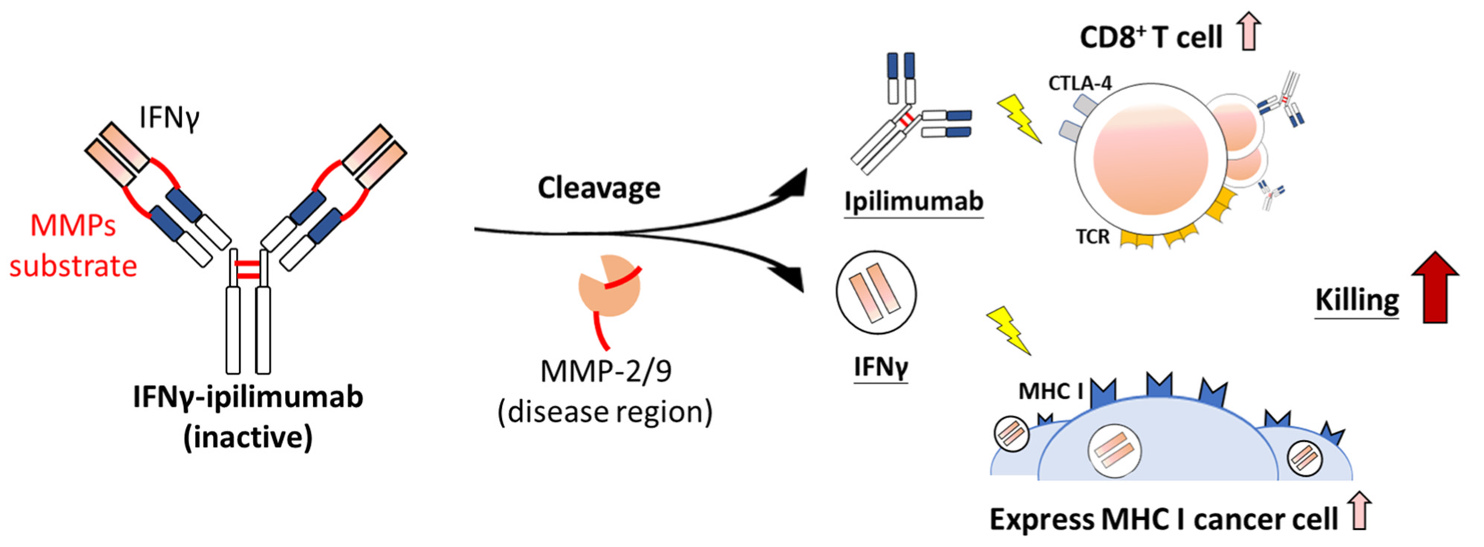
免疫檢查點抑制劑療法是一種前景廣闊的癌症治療策略,其中 Ipilimumab 因其能夠誘導細胞毒性 T 細胞的增殖和活化而受到廣泛關注。該療法透過與細胞毒 T 淋巴細胞相關抗原 4(Cytotoxic T Lymphocyte-Associated Antigen-4, CTLA-4)結合發揮作用。然而,Ipilimumab 可能引發全身性免疫相關不良反應和腫瘤免疫逃脫,從而限制其療效。本研究開發了IFNγ-ipilimumab,並確認添加IFNγ 不會改變 Ipilimumab 的基本特性。研究結果顯示,IFNγ-Ipilimumab 可以被基質金屬蛋白酶激活,從而促進 IFNγ 訊號傳導途徑,增強 T 細胞的細胞毒性。體內研究表明,IFNγ-Ipilimumab 能夠通過增加 CD8+ 和 CD4+ 淋巴球對大腸直腸癌的治療作用,更有效地浸潤腫瘤區域,並誘導腫瘤細胞中的 MHC-I 表現。接受 IFNγ-Ipilimumab 治療的小鼠顯示出更高的存活率和體重,且 CD4+ 和 CD8+ 淋巴細胞的活化率較低,器官損傷減少。總結來說,IFNγ-Ipilimumab 能夠提升 Ipilimumab 的療效,同時減少其副作用,未來有望成為免疫療法中用於活化局部癌細胞或免疫細胞的重要抗體,從而進一步提高癌症治療的效果並確保安全性。
ICB抗體藥物在臨床應用中面臨缺乏腫瘤選擇性及療效低的問題。合併使用IFNr雖能改善這些問題,但IFNr也存在缺乏腫瘤選擇性及易引發全身免疫反應的風險。為了解決這些挑戰,我們開發了雙前驅IFNr-ICB抗體鎖平台。這一平台構建了一種N端含有IFNx(干擾素)和MMP-2受質的雙前驅抗體。此抗體在血液中處於失活狀態,從而降低對器官(尤其是血液中)的副作用。一旦進入腫瘤微環境,該抗體會被MMP-2/9酵素裂解成活化態的ICB抗體和IFNx。這種設計通過增加腫瘤區IFNx的含量,提高了T細胞的浸潤,並促進腫瘤免疫原受器的表現,從而增強ICB抗體的療效,同時降低副作用。此外,這一平台具有廣泛的適應性,能根據不同ICB抗體的種類進行調整和更換,進一步提升其臨床應用的靈活性和效果。這種創新設計不僅解決了現有治療中的關鍵問題,還為未來的癌症免疫治療提供了一個強有力的工具。
圖形摘要
【研究團隊】
團隊成員:莊智弘
代表單位:高雄醫學大學 健康科學院 醫學檢驗生物技術學系
團隊簡介:
莊智弘副教授、黃奕中博士以及新藥開發暨價創研究中心的研究團隊共同發表了題為「Selective activation of IFNγ–ipilimumab enhances the therapeutic effect and safety of ipilimumab」的研究論文,該論文於2020年6月刊登在《International Journal of Biological Macromolecules》期刊上。這篇期刊的影響因子為8.2,並在應用化學 (CHEMISTRY, APPLIED) 領域中排名前8.10%。這項研究的重要性在於其揭示了IFNγ與ipilimumab選擇性激活後,能顯著提升ipilimumab的治療效果和安全性,為未來的癌症免疫治療提供了新的方向和更安全的選擇。研究刊登於高影響力的期刊,進一步強調了其在科學界的價值和影響力。
研究聯繫Email:a4132600@gmail.com
【論文資訊】
論文出處:Selective activation of IFNγ-ipilimumab enhances the therapeutic effect and safety of ipilimumab. Int J Biol Macromol. 2024 Apr;265(Pt 2):130945.
全文下載:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.130945
Development of dual precursor IFNr-Ipilimumab antibodies to improve the efficacy and safety of clinical cancer treatment
Development of dual precursor IFNr-Ipilimumab antibodies to improve the efficacy and safety of clinical cancer treatment
Immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy is a highly promising strategy for clinical treatment of cancer. Among these inhibitors, ipilimumab stands out for its ability to induce cytotoxic T cell proliferation and activation by binding to CTLA-4. However, ipilimumab also gives rise to systemic immune-related adverse effects and tumor immune evasion, limiting its effectiveness. Objectives: We developed IFNγ–ipilimumab and confirmed that the addition of INF-γ does not alter the fundamental properties of ipilimumab. Results: IFNγ–ipilimumab can be activated by matrix metalloproteinases, thereby promoting the IFNγ signaling pathway and enhancing the cytotoxicity of T cells. In vivo studies demonstrated that IFNγ–ipilimumab enhances the therapeutic effect of ipilimumab against colorectal cancer by increasing CD8+ and CD4+ lymphocyte infiltration into the tumor area and inducing MHC-I expression in tumor cells. Mice treated with IFNγ–ipilimumab showed higher survival rates and body weight, as well as lower CD4+ and CD8+ lymphocyte activation rates in the blood and reduced organ damage. Conclusion: IFNγ–ipilimumab improved the effectiveness of ipilimumab while reducing its side effects. It is likely that future immunotherapies would rely on such antibodies to activate local cancer cells or immune cells, thereby increasing the therapeutic effectiveness of cancer treatments and ensuring their safety.
Graphical Abstract
Research Team Members: Chuang Chih-Hung
Representative Department: Department of Medical Laboratory Science and Biotechnology, Kaohsiung Medical University
Introduction of Research Team:
Associate Professor Chuang CH, Dr. Huang YJ and the research team from the New Drug Development and Price Innovation Research Center jointly published a groundbreaking research paper titled "Selective activation of IFNγ–ipilimumab enhances the therapeutic effect and safety of ipilimumab." This significant study was published in the Apr 2024 issue of the "International Journal of Biological Macromolecules." The journal boasts an impressive impact factor of 8.2 and ranks in the top 8.10% in the field of applied chemistry (CHEMISTRY, APPLIED). The importance of this study lies in its revelation that the selective activation of IFNγ and ipilimumab can significantly improve the therapeutic effect and safety profile of ipilimumab. This discovery offers a new direction and a safer option for future cancer immunotherapy. The study's publication in such a high-impact journal underscores its value and influence within the scientific community, highlighting its potential to pave the way for advancements in cancer treatment.
Contact Email:a4132600@gmail.com
Publication: Journal. Year Month; Issue (Volume): Pages. Selective activation of IFNγ-ipilimumab enhances the therapeutic effect and safety of ipilimumab. Int J Biol Macromol. 2024 Apr;265(Pt 2):130945.
Full-Text Article: https://reurl.cc/z10Q06


