以西妥昔單抗作為第一線治療藥物的轉移型結直腸癌患者當RAS出現突變時的多中心研究
以西妥昔單抗作為第一線治療藥物的轉移型結直腸癌患者當RAS出現突變時的多中心研究
接受西妥昔單抗(Cetuximab)治療的患者,可能產生後天性的抗藥性,究其原因為絲裂元活化蛋白激酶(MAPK)通路出現突變,其中最主要是分子路徑中RAS基因由野生型突然轉變成突變型。血液中RAS基因的突變與腫瘤組織中RAS基因突變息息相關。目前以抽血方式來檢測RAS基因是否有突變,有可能成為常規臨床操作上的一種替代方法。本研究的目的是以血液中ctDNA輔助檢測工具檢測國人血漿中RAS基因由野生型轉變成突變型的盛行率以偵測接受以西妥昔單抗(Cetuximab)治療的患者,當RAS基因發生突變時分析腫瘤的反應與預測腫瘤對於抗EGFR藥物治療的效益。
本研究使用MassARRAY平台評估血漿中RAS基因的突變,血液樣本的採集點在納入符合收案條件時,第一線治療期間每3個月一次與疾病治療無效的2個星期內(如圖一)。研究的主要終點是病人接受西妥昔單抗(Cetuximab)作為第一線治療期間RAS基因的突變率,並觀察RAS基因突變與治療效果及存活間的相關性。
接受西妥昔單抗(Cetuximab)作為第一線治療的RAS基因突變率在國人約有9.3%,而RAS基因的突變時間比病人影像學上證實治療無效提早3個月。並且RAS基因突變的這次族群的病人,其無疾病進展存活率與整體存活率都有意義地比無突變的病人差(P值分別為0.002及0.027)。
本研究證明使用MassARRAY平台評估血漿中RAS基因的突變狀態,是檢測早期腫瘤治療反應與預測抗EGFR藥物效益的有效方法。本研究簡明的圖文摘要(如圖二)。
圖形摘要
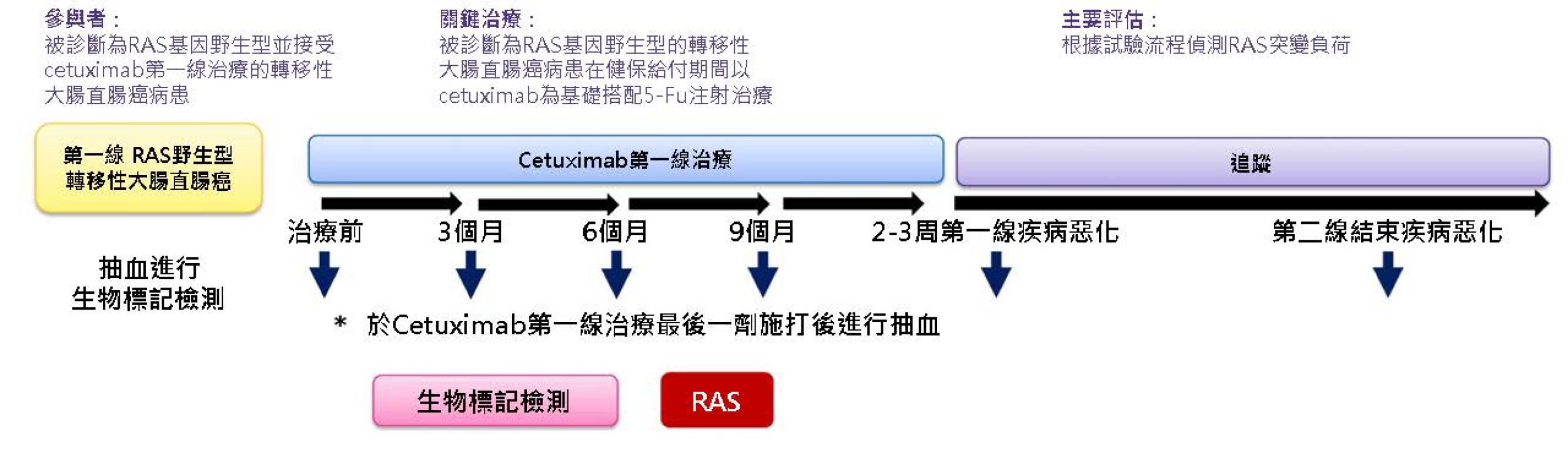
(圖一)
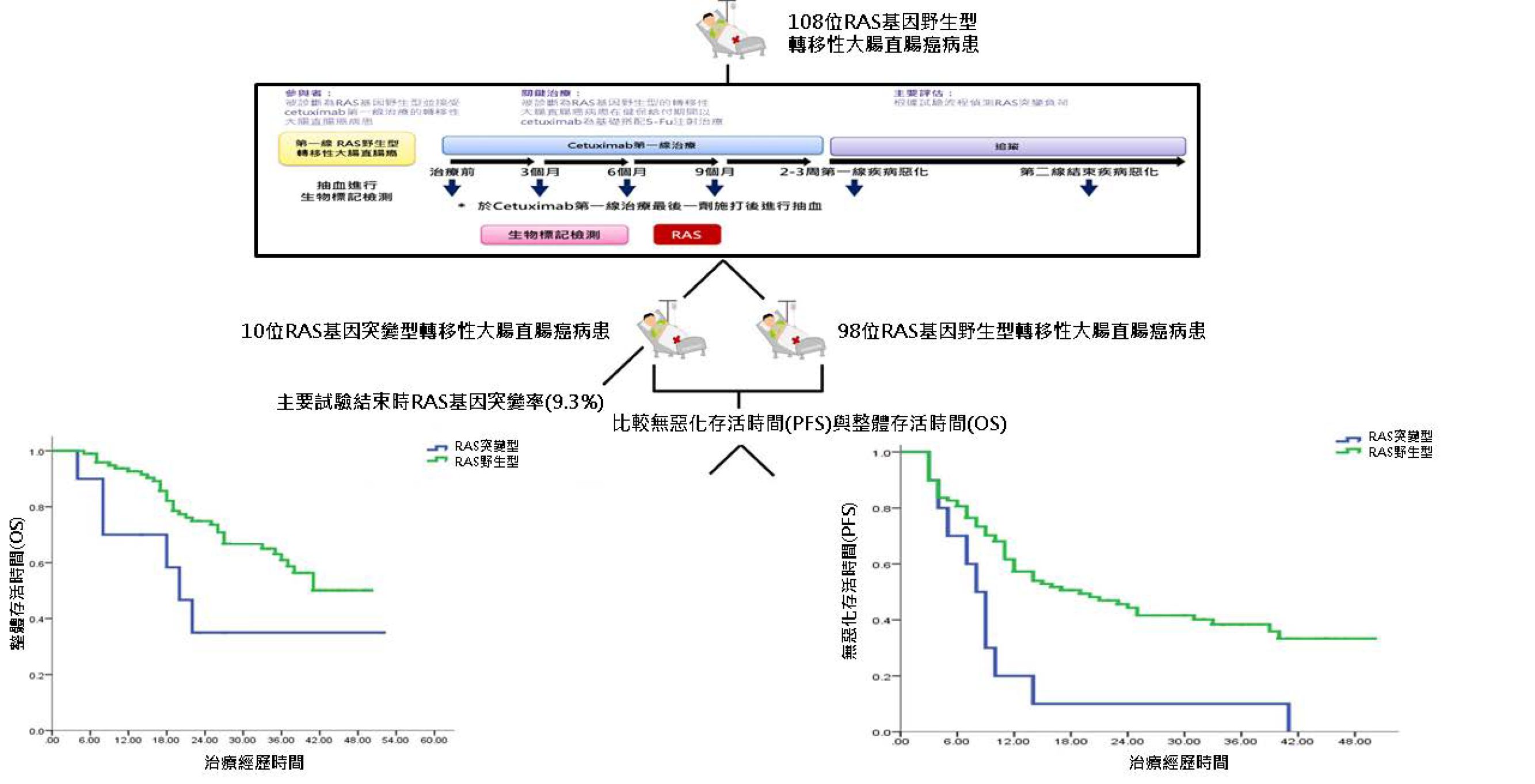
(圖二)
應用與亮點:
1.藉由簡單定期抽血的方式以得知RAS基因是否有突變?若有突變可以提早換藥以爭取有效的治療。
2.抽血檢測比侵犯性組織檢體的取得,可以讓病人更能接受且更不會排斥,以增加採檢率。
3.MassARRAY平台的檢測方法比NGS的方法成本更低,有助於臨床上推廣給更多病人。
【研究團隊】
團隊成員:王照元教授、陳立宗教授、蔡祥麟副教授、吳昌翰博士
代表單位:高雄醫學大學 癌症研究中心
團隊簡介:王照元教授團隊主要研究領域是大腸直腸癌及其治療,以結合基礎與臨床醫學腫瘤學於轉譯醫學及臨床潛在應用價值為主軸,重點發展技術涵蓋癌症基因檢測、腫瘤分子生物學、標靶藥物、免疫藥物與微創精準手術等多面向。
研究聯繫Email:cy614112@ms14.hinet.net; jawyuanwang@gmail.com
【論文資訊】
論文出處:Br J Cancer. 2023, 129, 947-955.
全文下載:http://doi.org/10.1038/s41416-023-02366-z
RAS mutations in patients with RAS wild-type mCRC receiving cetuximab as first-line therapy: a multicenter study
RAS mutations in patients with RAS wild-type mCRC receiving cetuximab as first-line therapy: a multicenter study
Patients received Cetuximab may develop acquired drug resistance. The reason is a mutation in the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway, the RAS gene is the most important mutation of the pathway. Moreover, mutations of RAS genes in blood are closely related to mutations in tumor tissues. Therefore, detection of RAS mutation with blood may now become an alternative to routine clinical practice. The purpose of this study is to use ctDNA auxiliary detection tools in blood to detect the prevalence of RAS mutation in plasma form the patients treated with cetuximab. We can predict the benefit of tumor response and anti-EGFR drug therapy.
The MassARRAY platform is used to evaluate the mutations of the RAS gene in plasma. Blood sample collection points are included when they meet the admission conditions, once every 3 months during the first-line treatment and within 2 weeks when the disease treatment is ineffective (Figure 1). The primary endpoint of the study is the mutation rate of the RAS gene during patients receiving cetuximab (Cetuximab) as first-line treatment, and to observe the correlation between RAS gene mutations and treatment efficacy and survival.
The RAS gene mutation rate among Chinese people who receive cetuximab (Cetuximab) as the first-line treatment is about 9.3%, and the RAS gene mutation time is 3 months earlier than the patient's imaging confirms that the treatment is ineffective. Moreover, the disease progression-free survival rate and overall survival rate of patients in this group with RAS gene mutations are significantly worse than those without mutations (P values are 0.002 and 0.027 respectively).
This study demonstrates that using the MassARRAY platform to assess the mutation status of the RAS gene in plasma can be an effective method for detecting early tumor treatment response and predicting the effectiveness of anti-EGFR drugs. A concise graphic abstract of this study is shown in Figure 2 .
Graphical Abstract
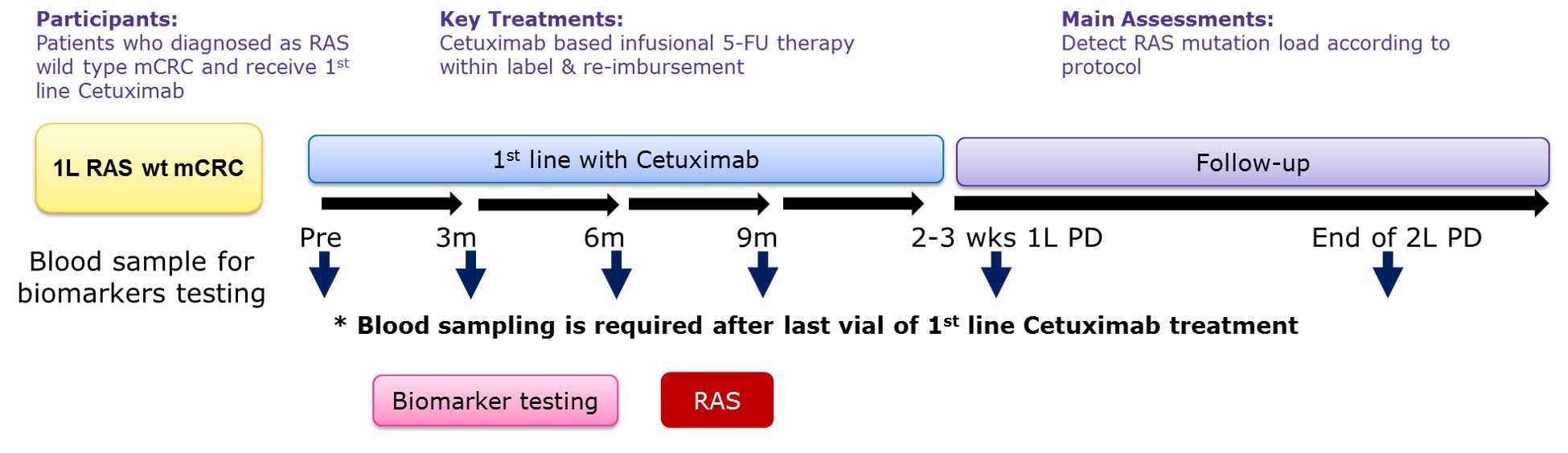
(Figure 1)
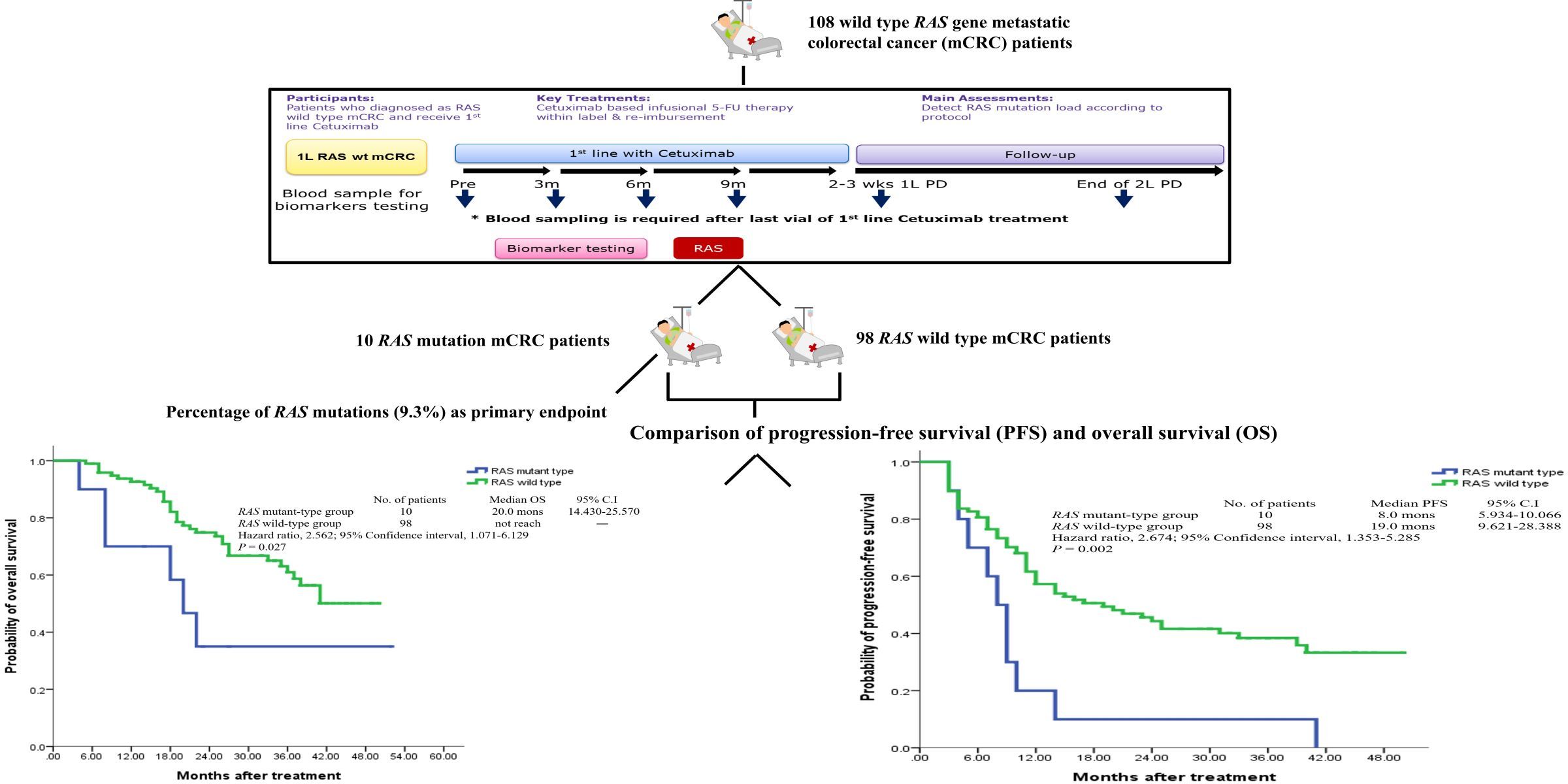
(Figure 2)
Application and Highlights:
1. By simply collect blood regularly, we can find out whether a mutation in the RAS gene. If mutation occur, the medication can be changed early for effective treatment.
2. Compared with the acquisition of invasive tissue specimens, blood testing can make patients more accepting, thereby increasing the testing rate.
3. The MassARRAY platform is cheaper than the NGS method, it’s helpful for clinical promotion.
Research Team Members:
Wang Jaw-Yuan Prof, Chen Li-Tzong Prof., Tsai Hsiang-Lin A.P., Wu Chang-Han phD.
Representative Department:
Center for Cancer Research, Kaohsiung Medical University
Introduction of Research Team:
The research field of Professor Wang Jaw-Yuan is colorectal cancer and its treatment. It focuses on combining basic and clinical medical oncology in translational medicine and clinical potential application value. The key development technologies include cancer gene detection, tumor molecular biology, targeted drugs, Immuno-drugs and minimally invasive precision surgery.
Contact Email:
cy614112@ms14.hinet.net; jawyuanwang@gmail.com
Publication: Br J Cancer. 2023, 129, 947-955.
Full-Text Article: http://doi.org/10.1038/s41416-023-02366-z




