神經因子對胰臟癌之影響—神經細胞所表現之神經降壓素與胰臟癌細胞所表現之信號素3A提升胰臟癌化而可受小分子藥物抑制
神經因子對胰臟癌之影響—神經細胞所表現之神經降壓素與胰臟癌細胞所表現之信號素3A提升胰臟癌化而可受小分子藥物抑制
胰臟癌仍為全球無聲殺手之一。即便手術、化學治療、標靶治療與新穎治療應用或研究於胰臟癌,但其於降低死亡率上效果有限。除胰臟癌細胞外,其腫瘤微環境於相關研究與治療同等重要,可見於多數回顧文獻討論纖維細胞與免疫細胞於此微環境中之角色。據其亞型纖維細胞可能於胰臟癌行提升或抑制之功效。據其族群免疫細胞於胰臟癌之影響可由CD8陽性T細胞行抑制或抗發炎(M2)型巨噬細胞行提升。除纖維細胞與免疫細胞外,神經細胞大多提升胰臟癌,且乃透過神經因子作為刺激因子與神經途徑作為傳播途徑。然神經因子於胰臟癌之預後與治療尚不清晰,因此可進一步研究。
透過系統化生物資訊分析,本團隊探得源自神經細胞之神經降壓素與源自胰臟癌細胞之信號素3A均預測胰臟癌較差預後,並可能受小分子抑制劑標定。神經降壓素受體1預測較差預後且可於胰臟癌細胞中探得。信號素3A受體—叢蛋白A1與纖毛蛋白2—與存活降低相關且可於神經細胞中探得。神經降壓素透過其受體1-PI3K-AKT訊息傳遞途徑提升胰臟癌細胞侵犯能力。信號素3A透過叢蛋白A1與纖毛蛋白2-MEK-ERK訊息傳遞途徑提升神經細胞移動。PI3K抑制劑與MEK抑制劑分別降低神經降壓素與信號素3A所造成之影響。於細胞實驗之二維與三維模式中均探得上述抑制效果。於動物實驗中抑制小鼠胰臟癌細胞株KPC之神經降壓素受體1或信號素3A達成降低原發與轉移腫瘤生長之效果。上述結果顯示神經因子於胰臟癌化之重要性且提供相關療法。
圖形摘要
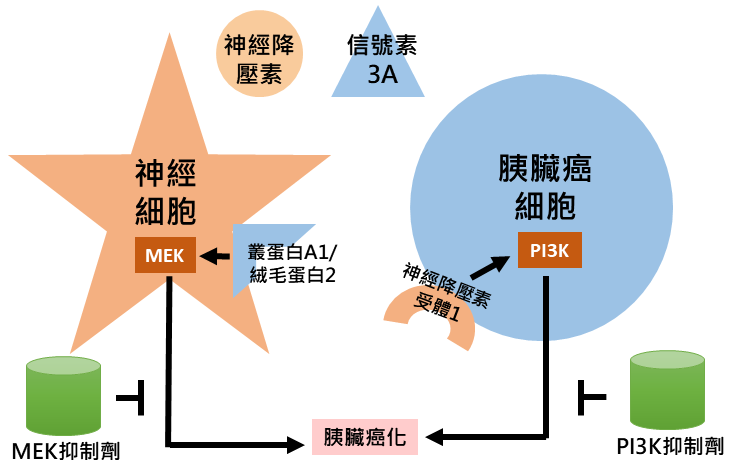
應用與亮點:
1. PI3K抑制劑可治療神經降壓素高表現之胰臟癌
2. MEK抑制劑可治療信號素3A高表現之胰臟癌
【研究團隊】
團隊成員:洪妤萱、陳立宗
代表單位:癌症研究中心
團隊簡介:該團隊隸屬於癌症研究中心,致力於胰腺癌以及其他胃腸道癌症的研究和潛在治療。
研究聯繫Email:leochen@nhri.edu.tw, yhhhung2021@gmail.com
【論文資訊】
論文出處:
1.Am J Cancer Res. 2024 Feb 15;14(2):448-466. eCollection 2024.
2.Am J Cancer Res. 2023 Aug 15;13(8):3417-3432. eCollection 2023.
全文下載:(網址)
1.https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38455426/
2.https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/37693128/
Neuron-derived neurotensin and pancreatic cancer-derived semaphorin 3A severe pancreatic cancer and are counteracted by small molecule inhibitors
Neuron-derived neurotensin and pancreatic cancer-derived semaphorin 3A severe pancreatic cancer and are counteracted by small molecule inhibitors
Pancreatic cancer is still one of the silent killers around the world. Even surgery, chemotherapy, targeted therapy, and novel therapy are available or under investigation for treatment, they provide limited success in reducing mortality. Besides pancreatic cancer cell, its microenvironment is equally important in research and treatment, as many reviews discuss the roles of fibroblast and immune cell in such environment. Depending on subtype, fibroblast may display both pro- or anti-tumor effects on pancreatic tumorigenesis. Depending on population of immune cell, pancreatic cancer formation is affected by CD8+ T cell for suppression or anti-inflammatory (M2) macrophage for promotion. In addition to fibroblast and immune cell, neuron is reported to mainly support pancreatic cancer by providing neural factor as stimulant and neural tract as route for dissemination. However, the prognostic power and therapeutic potential for neural factor in pancreatic cancer is less known, thus deserves further investigation.
By using systematic bioinformatic analyses we found factor neurotensin from neuron and semaphorin 3A from pancreatic cancer both predicted poor pancreatic cancer prognosis, and are potentially counteracted by small molecule inhibitors. The receptor for neurotensin, neurotensin receptor 1, predicted poor prognosis and is observed in pancreatic cancer. The receptors for semaphorin 3A, plexin A1 and neuropilin 2, associated with decreased survival and are observed in neuron. Neurotensin increased pancreatic cancer invasiveness via neurotensin receptor 1-PI3K -AKT axis. Semaphorin 3A increased neural migration via plexin A1/neuropilin 2-MEK-ERK axis. Inhibitor against PI3K or MEK counteracted the effect induced by neurotensin or semaphorin 3A, respectively. These inhibitions are observed in both 2D and 3D models in cell line experiment. In mouse experiment, knocking down neurotensin receptor 1 or semaphorin 3A in mouse pancreatic cancer cell line KPC led to decreased tumor growth of primary and/or secondary sites. These results suggested the importance of neural factor in pancreatic tumorigenesis and provided potential therapeutics for further treatment.
For future work we are dissecting the impact on pancreatic cancer immunity potentially resulted from neuron-derived neurotensin and pancreatic cancer-derived semaphorin 3A. This is due to the observation of differential recruitment of lymphocyte-like cell in mouse tumor of shLuc group. This phenomenon drove us to examine whether regulatory T cell or even other immune cell participate in pancreatic tumorigenesis driven by neurotensin or semaphorin 3A. Systematic bioinformatic analyses on datasets of public source or in-house one revealed that neurotensin associates with dysregulated myeloid cell population, while semaphorin 3A associates with dysregulated lymphoid cell population. Our cell line experiments preliminarily confirmed the changes of marker and/or factor of these immune cells being stimulated with neurotensin or semaphorin 3A. Besides further mechanistic dissection, we will stain mouse tumor of groups shLuc, shNTS, or shSEMA3A for markers of neuron, pancreatic cancer, myeloid cell, or lymphoid cell to see whether the association identified in bioinformatic analysis at mRNA level could be validated in tumors from mouse or even specimen at protein level. Further studies for mechanism, therapeutic, and in vivo confirmation will deepen our understanding of neural factor-regulated pancreatic tumorigenesis and its therapeutic potential for related research and potential treatment.
Graphical Abstract
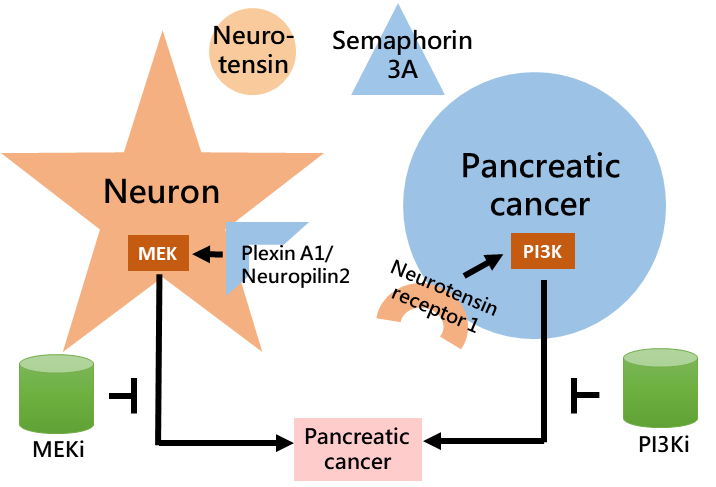
Application and Highlights:
1.PI3K inhibitor for neurotensin-high pancreatic cancer treatment
2.MEK inhibitor for semaphorin 3A-high pancreatic cancer treatment
Research Team Members: Yu-Hsuan Hung, Li-Tzong Chen
Representative Department: Center for Cancer Research
Introduction of Research Team:
This team is part of the Center for Cancer Research for research and potential treatment for pancreatic cancer as well as other gastrointestinal cancers.
Contact Email: leochen@nhri.edu.tw, yhhhung2021@gmail.com
Publication:
1.Am J Cancer Res. 2024 Feb 15;14(2):448-466. eCollection 2024.
2.Am J Cancer Res. 2023 Aug 15;13(8):3417-3432. eCollection 2023.
Full-Text Article:
1.https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38455426/
2.https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/37693128/


