環境物質-三聚氰胺-會造成慢性腎臟病患者的腎臟急速惡化
環境物質-三聚氰胺-會造成慢性腎臟病患者的腎臟急速惡化
慢性腎臟病是一個全球性的公共衛生問題。在台灣,每十人就有一人罹患慢性腎臟病,慢性腎臟病也擠身於台灣人口十大死因之一。腎臟是個沉默的器官,往往發生異常而不自覺,當有明顯症狀時已來到洗腎的十字路口,如何能提早並預防慢性腎臟病的發生及惡化,是政府機關及臨床照護人員努力的方向。造成慢性腎臟病的原因很多,仍有許多未知的病因造成慢性腎臟病的發生,除了糖尿病、高血壓、腎絲球腎炎等常見造成慢性腎臟病的原因外,日常生活接觸到的環境物質也可能誘發慢性腎臟病。
在2008年,中國發生毒奶粉事件,奶粉原料中被添加了三聚氰胺(melamine),造成嬰幼兒們腎結石,進而引發腎衰竭。在日常生活裡,三聚氰胺常被用來做成美耐皿餐具,即所謂的熱塑性塑膠產品,民眾在不知不覺裡食入或是接觸到過多的三聚氰胺,因此蔡宜純醫師、腎臟內科與環境醫學中心合作來探討三聚氰胺和慢性腎臟病預後進展的關聯性。研究團隊對293位早期慢性腎臟病(stage 1~3)進行長達七年的觀察,結果發現尿液三聚氰胺濃度較高的病人其血清肌酸酐較容易上升2倍、腎絲球過濾率下降速率較快,且腎絲球過濾率也容易在兩年內就下降30%。從本研究結果可知慢性腎臟病病人,其尿液三聚氰胺濃度和腎臟功能的快速惡化有顯著相關,尿液三聚氰胺濃度較高的病人有較差的臨床腎臟預後。此研究成果不但提供給政府機關三聚氰胺對腎臟影響的警訊,也提醒民眾減少生活中熱塑性塑膠產品之使用,進而維護腎臟的健康。
論文第一作者是醫學院教授蔡宜純醫師。通訊作者為環境醫學中心吳明蒼教授。感謝高醫附院腎臟內科團隊陳鴻鈞教授、黃尚志教授及邱怡文主任、及環境醫學中心團隊吳佳芳博士、劉家駒教授及謝翠娟副教授的協助。
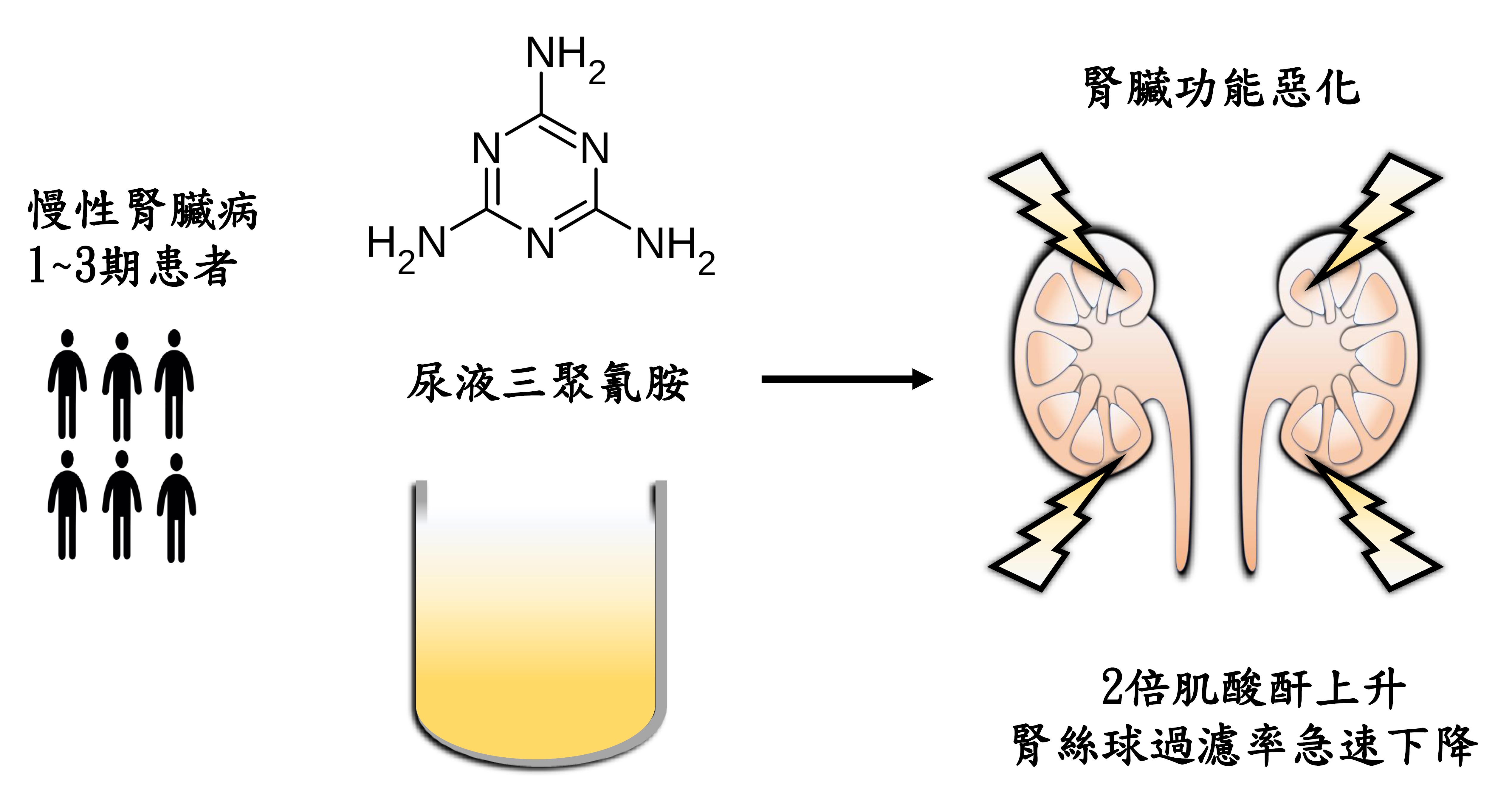
圖示來源: https://cjasn.asnjournals.org/content/14/8/1133.long
圖說: 293位早期慢性腎臟病(1~3期)病人,在7年的觀察期中,尿液裡三聚氰胺濃度較高的患者與濃度較低的患者相比,腎臟功能容易快速惡化。
Urinary Melamine Levels and Progression of Chronic Kidney Disease
Urinary Melamine Levels and Progression of Chronic Kidney Disease
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) is a global public health problem. The etiology of development and progression of early CKD is multifactorial. Some cross-sectional studies have associated environmental melamine exposure with kidney diseases, but evidence is limited. Professor Yi-Chun Tsai and colleagues at Division of Nephrology, Kaohsiung Medical University Hospital, and Research Center for Environmental Medicine, Kaohsiung Medical University demonstrated urinary melamine as a predictor of rapid decline in kidney function in patients with CKD stages 1-3.
This is the first study to find an association between environmental melamine exposure and adverse kidney outcomes in a clinical setting. Over a median follow-up period of 7.0 years, subjects in the highest tertile of urinary melamine level had a 2.30 hazard risk for doubling of serum creatinine, compared to those in the lowest tertile. Similar significant dose-response results were found in estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) decline > 3 ml/min/1.73m2 per year and 30% decline in eGFR in the first two years. Urinary melamine level is significantly associated with kidney function deterioration in early stage CKD patients. Moreover, research team performed subgroup analysis and demonstrated the association between urinary melamine and kidney function deterioration in subjects with baseline eGFR ≥ 45 ml/min/1.73m2 and in subjects with diabetes mellitus.
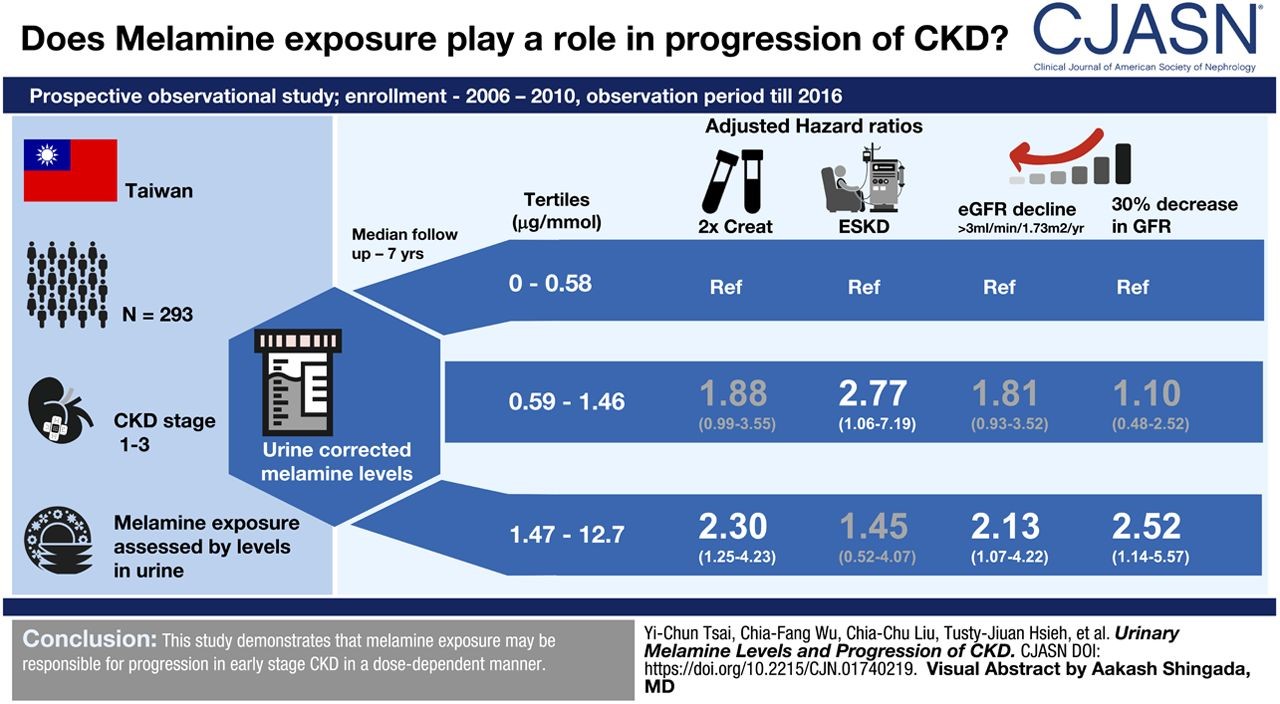
CKD patients with the highest tertile of urinary melamine was associated with rapid decline in kidney function including doubling of serum creatinine, estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) decline > 3 ml/min/1.73m2 per year and 30% decline in eGFR in the first two years compared to those in the lowest tertile.Figure source was from https://cjasn.asnjournals.org/content/14/8/1133.long
This article-“Urinary Melamine Levels and Progression of Chronic Kidney Disease” , written by Rept. Author Professor Yi-Chun Tsai, from College of Medicine, is award for Kaohsiung Medical University 2019 Monthly Excellent Paper Award in Aug. The authors of this article include Dr. Yi-Chun Tsai and her colleagues at Division of Nephrology, Kaohsiung Medical University Hospital (Dr. Yi-Wen Chiu, Professor Shang-Jyh Hwang, and Professor Dr. Hung-Chun Chen and colleagues at Research Center for Environmental Medicine, Kaohsiung Medical University Hospital (Professor Ming-Tsang Wu, PhD Chia-Fang Wu, Professor Chia-Chu Liu, and Associate Professor Tusty-Jiuan Hsieh).
This study was published online in Clinical Journal of American Society of Nephrology the 7th August 2019. The full research article entitled “ Urinary Melamine Levels and Progression of Chronic Kidney Disease”is available online through CJASN at https://cjasn.asnjournals.org/content/14/8/1133.long.


