C型肝炎病毒的核心蛋白與腸道特異性同源盒蛋白交互作用於肝病中扮演的角色
C型肝炎病毒的核心蛋白與腸道特異性同源盒蛋白交互作用於肝病中扮演的角色
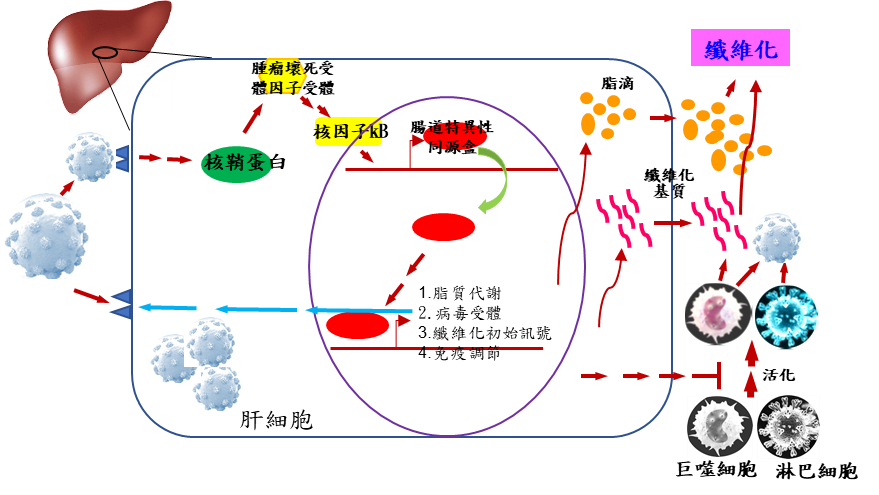
C型肝炎病毒(HCV)感染產生慢性肝疾病對本國人來說是重要的公共衛生議題。然而,關於病毒如何重塑對於肝病理環境的代謝和免疫反應的研究目前是有限的。我們的轉錄體學研究證明,HCV 核心蛋白(core protein)與腸道特異性同源盒(ISX) 作用可促進代謝重塑、肝纖維化形成以及免疫調節(影響PD-L1 和B7-2等表現),這些對於肝炎的發生息息相關。並在基因轉殖小鼠模型中,也證實HCV 核心蛋白-ISX 作用增強了代謝紊亂(特別是脂質和葡萄糖代謝)和免疫抑制,最後在高脂飲食 (HFD) 誘導的疾病模型中也增強了慢性肝纖維化。
從機制來看,帶有 HCV 的JFH-1 複製子的細胞活化 ISX,從而透過核心蛋白誘導的核因子-κB 訊號傳導促進細胞代謝、纖維化和免疫調節。 反之,具有特異性 ISX shRNAi 的細胞可抑制 HCV 核心蛋白誘導的代謝紊亂和免疫抑制。
我們在臨床研究中也發現受到C型肝炎病毒感染的肝炎患者的核心蛋白與ISX、IDOs、PD-L1、B7-2表現有顯著相關。 因此,本研究發現C型肝炎病毒核心蛋白與ISX作用機制,對慢性肝病發展重要性,可作為臨床治療標靶參考標記。
圖形摘要:
應用與亮點:
1. C型肝炎病毒的核心蛋白(core protein)與腸道特異性同源盒(ISX)作用可促進代謝重塑、肝纖維化形成以及免疫調節。
2. 腸道特異性同源盒(ISX)是C型肝炎病毒導致肝病的關鍵因子
研究團隊
團隊成員: 邱世欣教授、許世賢教授、王麗婷助理研究員
代表單位: 高雄醫學大學應用基因體研究中心
聯絡信箱: genomics@kmu.edu.tw
論文資訊
論文出處: Adv Sci (Weinh). 2023 Aug;10(23):e2300644.
全文下載: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC10427408/
The role of the interaction between hepatitis C virus core protein and intestinal-specific homeobox (ISX) protein in liver disease.
The role of the interaction between hepatitis C virus core protein and intestinal-specific homeobox (ISX) protein in liver disease.
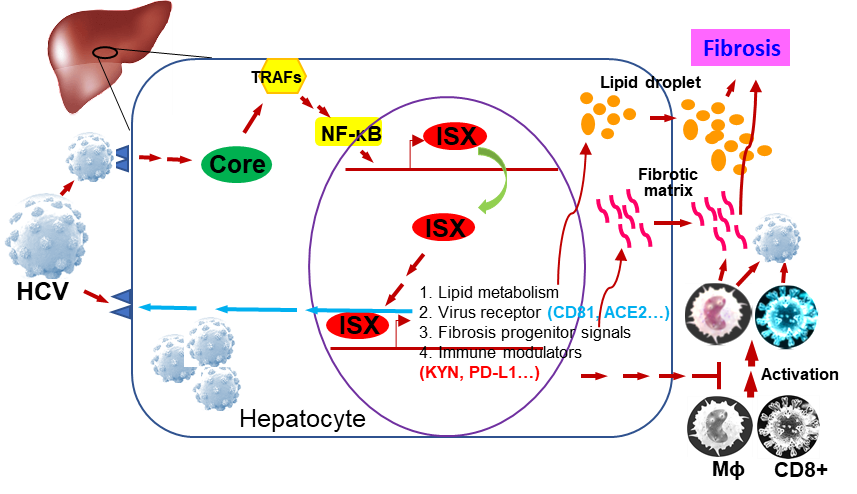
Chronic liver disease caused by hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection is an important public health issue for the Chinese population. However, research on how viruses reshape metabolic and immune responses to liver pathological environments is currently limited. Our transcriptome studies have proven that the interaction between HCV core protein and intestinal-specific homeobox (ISX) can promote metabolic remodeling, liver fibrosis formation, and immune regulation (affecting PD-L1 and B7-2, etc. manifestations), which are closely related to the occurrence of hepatitis. In the genetically modified mouse model, it was also confirmed that the effect of HCV core protein-ISX enhanced metabolic disorders (especially lipid and glucose metabolism) and immunosuppression, and finally was also enhanced chronic liver fibrosis in high-fat diet (HFD)-induced disease models. Mechanistically, cells harboring the JFH-1 replicon of HCV activate ISX, thereby promoting cellular metabolism, fibrosis, and immune regulation through core protein-induced NF-κB signaling. Conversely, cells with specific ISX shRNAi suppressed HCV core protein-induced metabolic disorders and immunosuppression. In clinical studies, we also found that the core protein of hepatitis patients infected with hepatitis C virus is significantly related to the expression of ISX, IDOs, PD-L1, and B7-2. Therefore, this study found that the mechanism of action of hepatitis C virus core protein and ISX is important to the development of chronic liver disease and can be used as a reference marker for clinical treatment targets.
Graphical Abstract:
Application and Highlights:
1. The interaction between the core protein of hepatitis C virus and the intestinal-specific homeobox (ISX) can promote metabolic remodeling, liver fibrosis formation and immune regulation.
2. Intestinal-specific homeobox (ISX) is a key factor in liver disease caused by hepatitis C virus.
Main researcher :
Professor Shih‐Hsien Hsu, Center of Applied Genomics, Kaohsiung Medical University
Main authors’email :genomics@kmu.edu.tw
Publication:
Adv Sci (Weinh). 2023 Aug;10(23):e2300644.
Full-Text Article:
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC10427408/


