數位學習之創新變革—高醫大心電圖互動式電子書能有效提升護生學習效率
數位學習之創新變革—高醫大心電圖互動式電子書能有效提升護生學習效率
重症護理學在護理系的課程中,是一門比較艱深的課程,其中心電圖是學生認為最困難的單元,目前常見的心電圖教學法有課堂講授、工作坊、擬真學習等,然而在疫情時代,這些需要面對面教學的方法就不太適用,因此發展有效的數位學習教材來提升學生學習成效,實為至關重要的教學任務。
高醫護理系教師依據學習動機理論,發展心電圖互動式電子書,功能包含目錄超連結、多媒體、遮罩功能、互動式練習題及強制學習等。並將之應用於重症護理教學中,學生可經由網路或手機應用程式隨時隨地進行個人化的學習,增進自主學習。在經過兩年的研究,發現使用互動式電子書的學生及使用傳統紙本講義的學生,在考試成績上雖無顯著差異,但在學習時間上卻有顯著差異。使用互動式電子書的學生用較少的學習時間,卻能達到相似的學習成效,也就是說,使用心電圖互動式電子書可以幫助學生更有效率地學習複雜抽象的概念。
在學習滿意度方面,大部分的學生都滿意互動式電子書對提升其學習動機(73.1%)、自主學習(77%)、和學習成效(88.5%)的幫助。訪談學生時,學生更表示電子書在學習方便性、有效性及擴充性是讓他們最滿意的。雖然有少數學生在使用上會遭遇到一些技術上的問題,但教師若能提供即時的幫助,可降低學生因技術困難而產生的學習挫折。未來醫護教育中,可以更廣泛的應用互動式電子書來提升學生的學習效率及滿意度。
圖形摘要
〈電子書頁面範例〉
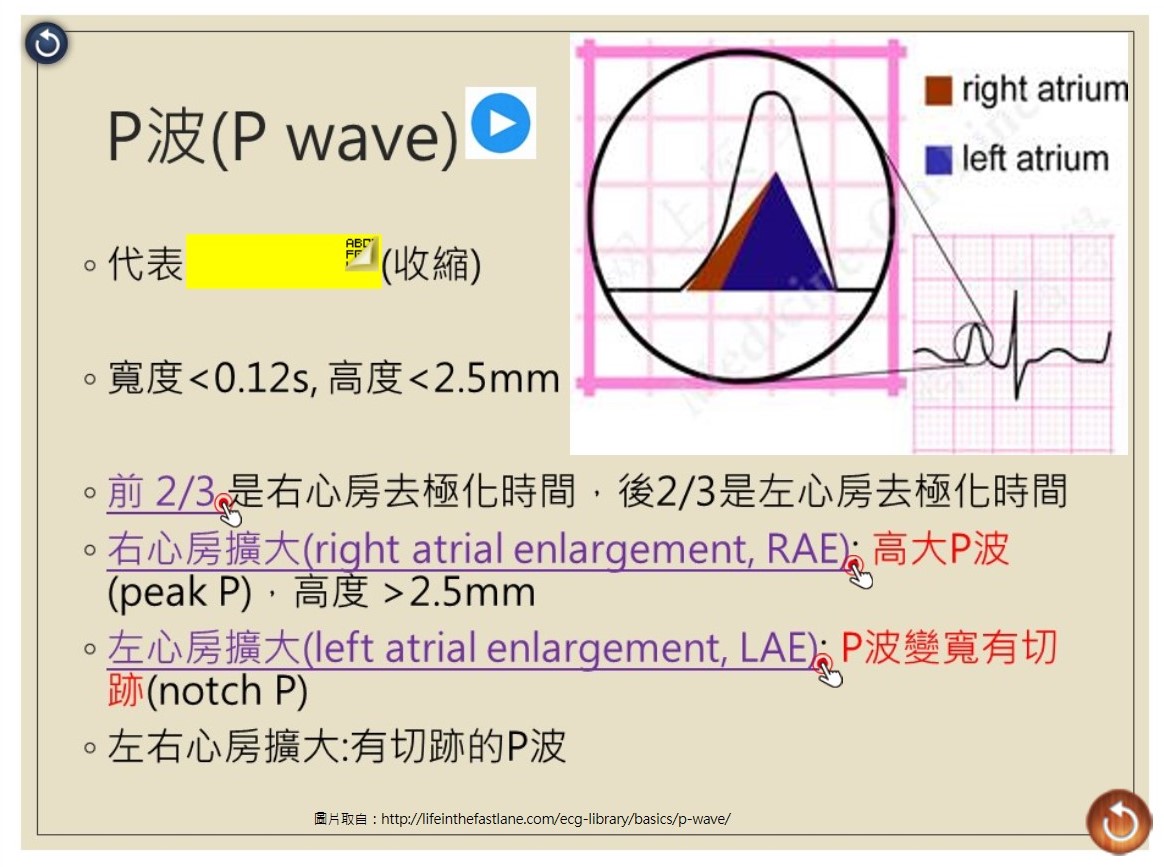
應用與亮點:
1.根據動機理論製作的互動式電子書可作為有效提升醫護學生線上學習成效的教學工具。
2.互動式電子書可應用於其他醫護課程或做為臨床醫護人員線上在職教育的學習教材。
3.未來可建立互動式電子書線上圖書館供學生做跨領域學習或供社會大眾使用,提升其利用率。
4.未來可根據學生或業界需求,結合遊戲學習,發展更好的互動式教學教材。
【研究團隊】
團隊成員:劉怡 Yi Liu、李碧娥 Bi-oh Lee、周碧玲 Pi-Ling Chou
代表單位:護理系
團隊簡介;
劉怡副教授關注護理教育及護理職場議題,獲得108教育部教學實踐計畫醫護學門績優計畫。李碧娥教授為外傷照護、護理教育及跨領域研究的專家。周碧玲副教授為心衰竭照護、癌因性疼痛及創新課程的專家。
研究聯繫Email:gn94yliu@kmu.edu.tw
【論文資訊】
論文出處:
Nurse Education Today, 90 (July), 104424 (2019 SSCI, Nursing, IF:2.49, 7/121= 5.78%)
全文下載:
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0260691719316399?via%3Dihub
The innovation of digital learning-the EGC interative eBook can promote nursing student's learning effciency
The innovation of digital learning-the EGC interative eBook can promote nursing student's learning effciency
Critical care nursing is a difficult course in the nursing curriculum. Electrocardiography (ECG) interpretation has been considered the most difficult since the concept of ECG is complex and abstract. Currently, the common teaching methods for ECG learning include lectures, workshops, and simulation, etc. However, in the pandemic era, the face-to-face teaching method may not be applicable. It is important to develop digital learning material to enhance students’ digital learning.
To enhance nursing students’ digital learning effect, an interactive ECG eBook based on motivation theory was developed. The interactive functions included hyperlink index, multimedia, cover-up, interactive exercises, and forced learning, etc. This eBook was applied in the critical care nursing course. Students could have individualized learning anytime and anywhere via the internet or the mobile application program, which would further enhance students’ self-directed learning. After a two-year comparison study, it was found that the learning achievements were not significantly different between the group using the eBook and the group using traditional paper handouts. However, the study time was significantly less in the eBook group. It indicated that nursing students could learn in a more efficient way using an interactive e-book.
Regarding students’ learning satisfaction, most nursing students were satisfied with the ECG interactive eBook for promoting their learning motivation (73.1%), self-directed learning (77%), and learning achievement (88.5%). In the interview, students reported they were most satisfied with the convenience, effectiveness, and extensiveness of the eBook. Few students mentioned that some technical problems were encountered. It was suggested that teachers need to provide prompt assistance to help students with technical difficulties to decrease their frustration. In the future, the application of interactive eBooks in medical and nursing education should be extensively encouraged to promote students’ learning efficiency and satisfaction.
Graphical Abstract

Application and Highlights:
1.The interactive eBook based on the motivation theory can be a learning tool for promotingstudents digital learning efficiency.
2.The interactive eBook can be applied to other medical and nursing courses or to continuing education courses for clinical health care providers.
3.In school, a digital library for interaction eBooks can be built for students’interdisciplinary learning or for the public to promote the usage of digital learning materials.
4.The interactive eBooks can further combine with gamification learning to create advanced interactive learning based on the needs of students and fields.
Research Team Members: Yi Liu, Bih-O Lee, and Pi-Ling Chou
Representative Department: School of Nursing
Introduction of Research Team:
Yi Liu (associate professor) focuses on nursing education and workplace issues and was awarded “Excellent Performance” in the Ministry of Education Teaching Practice Research program. Bih-O Lee (professor) is an expert in trauma, nursing education, and interdisciplinary research. Pi-Ling Chou (associate professor) is an expert in heart failure, cancer pain, and innovative education.
Contact Email: gn94yliu@kmu.edu.tw
Publication:
Nurse Education Today, 90 (July), 104424 (2019 SSCI, Nursing, IF:2.49, 7/121= 5.78%)
Full-Text Article: (URL)
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0260691719316399?via%3Dihub

